Niobium has a melting point of 4474 F, which is 256 degrees lower than that of molybdenum. Pure niobium is very ductile and can be cold worked easily at room temperature. As with tantalum, large reductions are possible between anneals.
The density of niobium is only slightly greater than that of steel and considerably less than that of other refractory metals with higher melting points. Because of this, and the high-temperature strength and favorable nuclear properties, there has been extensive development of niobium base alloys for airborne nuclear reactors.
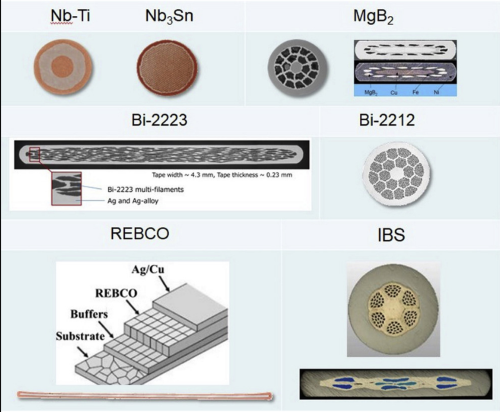
Introduction Niobium possesses exceptional properties and multiple applications. This elemental stands out among transition metals. Particularly, it can withstand extreme temperatures, exceeding 2,400 degrees Celsius. Therefore, it can endure the most challenging conditions. Niobium’s uses extend across diverse industries. It works well in alloying with other metals, especially in the creation of superconducting materials. This […]

Introduction As energy demand increases and environmental concern rises, people start to search for new renewable energy sources such as wind, solar, and geothermal power. Lots of advanced techniques including artificial photosynthesis and water-splitting reaction are developed to generate solar fuels. Moreover, photoactive semiconductor materials like Niobium are also utilized to enhance the efficiency of […]
Tags: How Does Artificial Photosynthesis Happen, How Does Water Splitting Occur, Niobium-based Photoactive Water Splitting Catalyst, Uses of Niobium
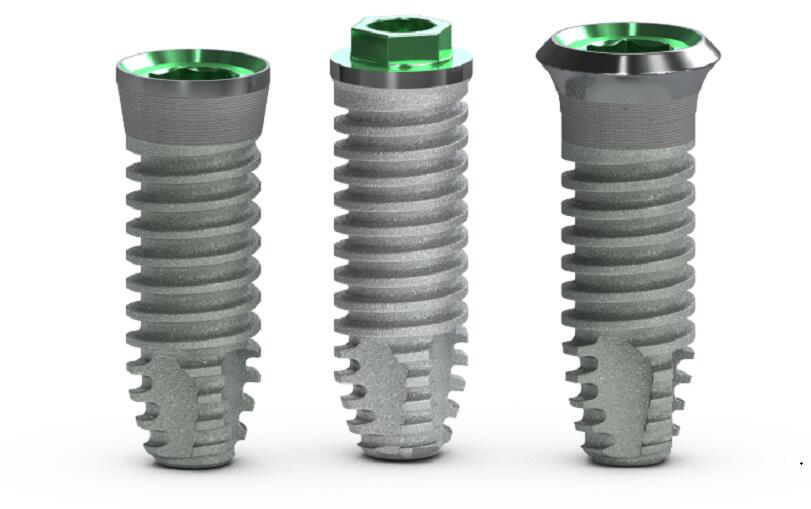

Application of Niobium in Stomatology Niobium is a shiny gray metal with a melting point of 2468 ℃ and a boiling point of 4742 ℃. Due to its excellent physical and chemical properties, niobium has a wide range of applications in many fields. In this article, let’s take a deeper look at the application of niobium […]
Tags: Advanced Refractory Metals, Application of Niobium, Application of Niobium in Oral Implantation, Application of Niobium in Oral Medicine, Application of Niobium in Oral Radiation, Application of Niobium in Oral Restoration, Application of Niobium in Oral Surgery, Application of Niobium in Orthodontics, ARM, Niobium, refractory alloys, Refractory Metals

Application of Niobium in the Steel Industry The application fields of niobium can basically be divided into the steel industry and the non-steel industry. The former accounts for more than 85% of the world’s niobium consumption, while the latter accounts for less than 15%. In this article, let’s take a closer look at the application of […]
Tags: Advanced Refractory Metals, Application of Niobium, Application of Niobium in Alloy Steel, Application of Niobium in Cast Iron, ARM, Niobium, niobium bars, Niobium in the Steel Industry, Refractory Metal, Types of Refractory Metals

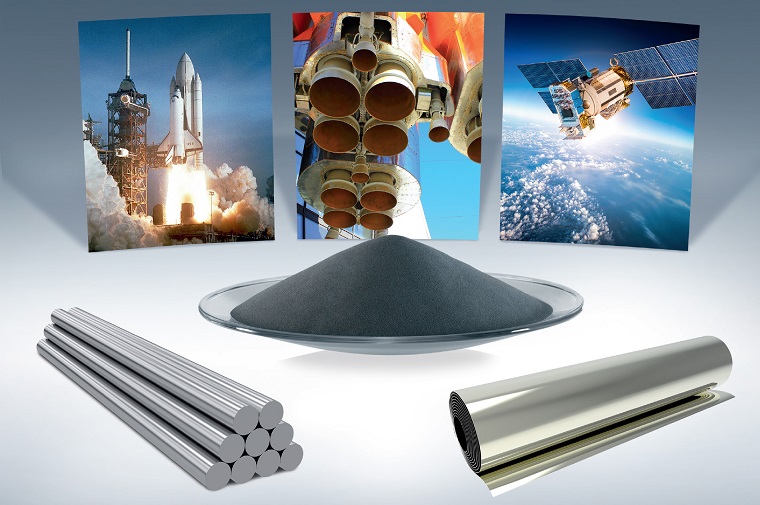
Refractory Metals & Alloys for Aerospace Refractory metals refer to metals with melting points above 2000°C. They include tungsten, molybdenum, tantalum, niobium, rhenium, and vanadium. The common characteristics of refractory metals and their alloys are high melting point, high strength at high temperatures, and good corrosion resistance to liquid metals. Their use temperature range is 1100~320℃, […]
Tags: Advanced Refractory Metals, ARM, Molybdenum, Molybdenum Alloys, Niobium, Niobium alloys, refractory alloys, Refractory Metals, refractory metals & alloys, rhenium, Rhenium Alloys, tantalum, tantalum alloys, Tungsten, Tungsten alloys, tungsten-copper composite material, Vanadium, vanadium alloys
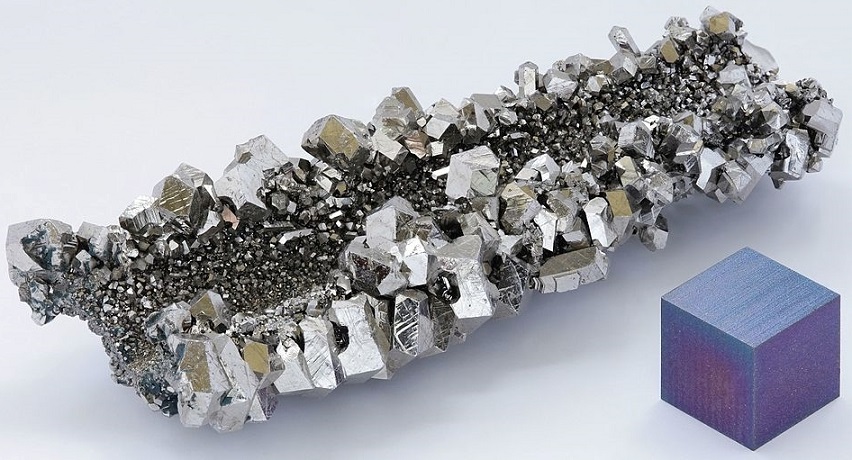

10 Important Uses of Niobium Niobium is a rare metal with a high melting point, silvery gray color, soft texture, and good ductility. The density of niobium is 8.57g / cm³, the melting point is 2477 ° C, and the boiling point is 4744 ° C. Thanks to its good superconductivity, high melting point, corrosion resistance, and […]
Tags: 10 Important Uses of Niobium, 10 Uses of Niobium, Advanced Refractory Metals, Important Uses of Niobium, metal with a high melting point, Niobium, Refractory Metals, The Uses of Niobium in the Aerospace Industry, The Uses of Niobium in the Atomic Energy Industry, The Uses of Niobium in the Chemical Industry, The Uses of Niobium in the Electronics Industry, The Uses of Niobium in the Foundry Industry, The Uses of Niobium in the Lighting Industry, The Uses of Niobium in the Medical Field, The Uses of Niobium in the Metal Industry, The Uses of Niobium in the Optical Industry, The Uses of Niobium in the Superconducting Materials Industry, Tungsten, Use of Niobium, Uses of Niobium
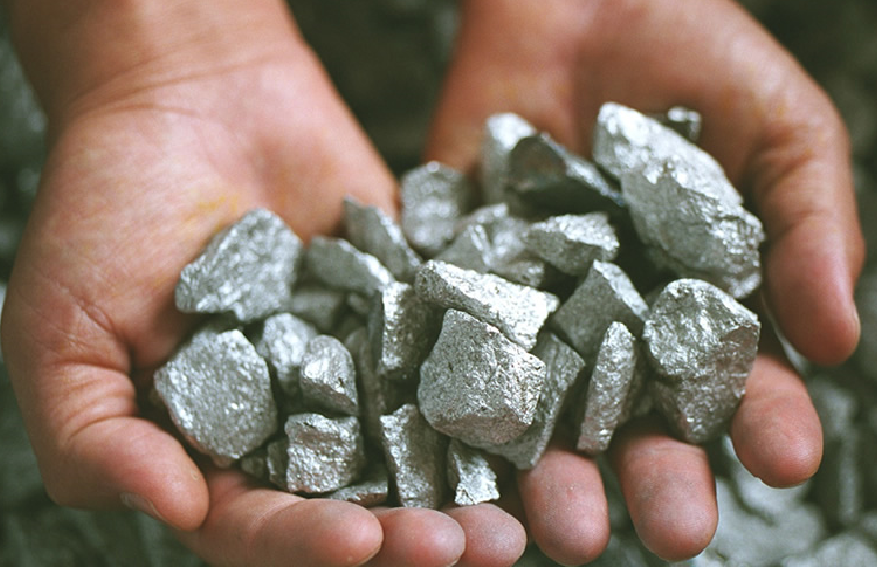

What Is Niobium Used For In Everyday Life? Niobium has a melting point of 4474℉, which is 256 degrees lower than that of molybdenum. The development of niobium metal and its alloys for elevated-temperature structural applications was started only a few years ago, but considerable progress has been made since then. One factor that has been […]
Tags: Niobium, Niobium alloys, niobium metal, Pure niobium, Refractory Metal, Refractory Metals, What Is Niobium, What Is Niobium Used For In Everyday Life?
The Role of Niobium in Superalloys Refractory elements are important alloying additions in both nickel-base and iron-nickel-base superalloys. They are responsible for the increased high-temperature mechanical properties present in current superalloy systems. In this article, we’ll take a look at the role of niobium in superalloys. It has long been established that nickel-base and iron-nickel-base […]
Tags: Advanced Refractory Metals, Nickel, Niobium, Niobium in Superalloys, Refractory elements, Refractory Metals, superalloy, The Role of Niobium in Superalloys
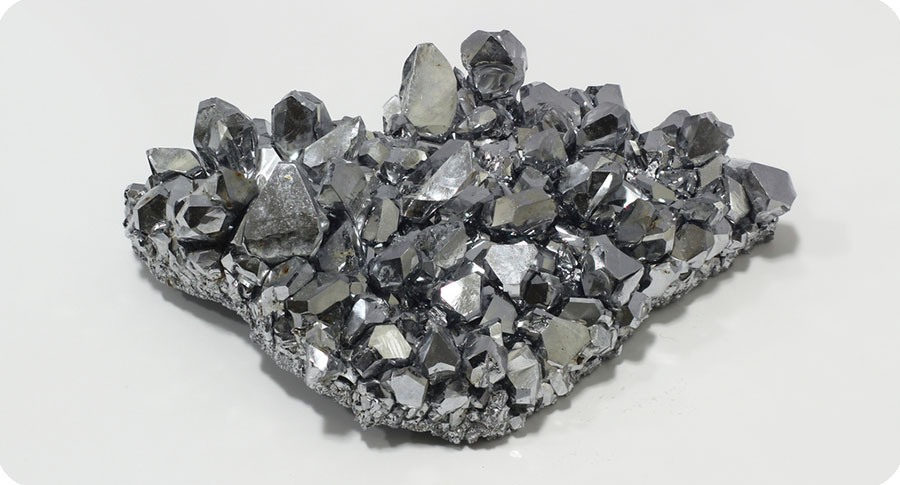

Niobium – A Material for Innovations with Great Future Potential In this article, we will introduce niobium, a material for innovations with great future potential. In actual fact, niobium, like all other metals, is gray. However, by applying a pacifying oxide layer, we allow our metal to gleam in a beautiful array of colors. Niobium is […]
Tags: Advanced Refractory Metals, Metal with High Melting Point, Niobium, Niobium A Material for Innovations, Niobium materials, Pure niobium, Refractory Metals, tantalum
Copyright © 1994-2024 Advanced Refractory Metals owned by Oceania International LLC, All Rights Reserved.