The term ‘refractory metal’ is used to describe a group of metal elements that have exceptionally high melting points and are resistant to wear, corrosion, and deformation.
Industrial uses of the term refractory metal most often refer to five commonly used elements:
Molybdenum (Mo)
Niobium (Nb)
Rhenium (Re)
Tantalum (Ta)
Tungsten (W)
The identifying feature of refractory metals is their resistance to heat. The five industrial refractory metals all have melting points in excess of 3632°F (2000°C).

Understanding Kinetic Energy Penetrator A Kinetic Energy Penetrator (KEP) is a type of ammunition designed primarily to penetrate heavy armor, such as that found on tanks and fortifications. Unlike explosive munitions, KEPs rely on the kinetic energy generated by their high speed and the density of the materials they are made from to achieve penetration. […]

Introduction In the world of materials science, extreme heat-resistant materials play a critical role in various high-temperature applications ranging from aerospace engineering to industrial furnaces. These materials are specially designed to withstand intense heat without losing their structural integrity. This article delves into the types of extreme heat-resistant materials and provides a comparative analysis of […]
Tags: Extreme Heat-Resistant Materials, heat resistant alloy, Heat Resistant Material, heta resistant metal, melting point
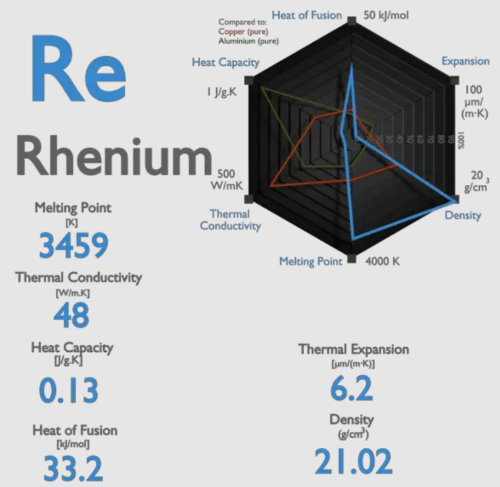
Introduction Rhenium may not be a household name, but in the world of science and industry, it stands out for its astonishingly high melting point of approximately 3,180 degrees Celsius. This often-overlooked metal plays a vital role in a wide range of applications. We’ll explore its ability to withstand extreme environments in this article. What […]
Tags: High Melting Points, Metals, rhenium

Introduction Tantalum-tungsten (Ta10W) powders have gained significant attention in various industries for their exceptional properties and versatile applications. These powders, composed of a tantalum and tungsten alloy, offer a unique combination of strength, high-temperature resistance, excellent corrosion resistance, and other desirable characteristics. In this article, we will explore their potential and their diverse range of […]
Tags: Aerospace, Biocompatibility, Chemical Applications, corrosion resistance, Defense, Electronics, Energy, Exceptional Strength, High-Temperature Resistance, Medical, Ta10W Powder

Introduction The field of manufacturing has witnessed significant advancements over the years, driven by the need for innovative and high-performance materials. Ta10W powders, a tantalum-tungsten alloy, have emerged as a game-changing material that meets the demands of modern manufacturing. With their unique properties and versatility, Ta10W powders have paved the way for enhanced performance, efficiency, […]
Tags: Additive Manufacturing, Advancements, Modern Manufacturing, Ta10W Powder

Introduction The glass manufacturing industry is boosting with a market of 106.44 billion dollars in 2021[1], and millions of tons of glass are produced every day using molybdenum electrodes and other agents. Here, we are going to focus on glass melting and the molybdenum electrodes it employs. Hope that you can have a better understanding […]
Tags: glass melting furnace, Molybdenum Electrodes, Molybdenum Electrodes for Glass Furnaces, The Development of Glass Melting, What Are Electrode Materials, What Are Molybdenum Electrodes, What Is Glass Melting

What Is Thermal Conductivity? Thermal conductivity (denoted by k, λ, or κ) refers to a material’s ability to conduct heat at specific temperature and pressure, and it is measured in W/m•K (watts per meter-Kelvin). Highly thermally conductive materials are used to make heat sinks. Materials that transfer heat slowly act as excellent insulators. Different materials […]
Tags: aluminum, Aluminum Nitride, Copper, gold, Graphite, Highly Thermally Conductive Materials, quality metals and alloys, Silicon carbide, silver, Tungsten, Zinc

1. Introduction to Alloys An alloy is a blend of 2 or more chemical elements, one of which is supposed to be metal. Different substances of controlled amount are added to a metal to form alloys with desirable properties. Examples of alloys like stainless steel, bronze, and brass are applied to various fields including construction, […]
Tags: Introduction to Alloys, Melting Point Diagrams of An Compound, Melting Points of Alloys, The Melting Point and Melting Range, The Melting Point of An Alloy Is Lower

Introduction The crust is the outermost layer of the Earth, making up 1% of the planet. It is composed of solid rocks and minerals formed, which are usually slowly formed over a long period of time. A range of elements can be found in the Earth’s crust, among which 7 of the 10 most abundant […]
Tags: 7 Most Abundant Metal Elements in Earth’s Crust, 7 Most Abundant Metal Elements in the Earth’s Crust, Aluminum Everywhere, Iron - the Most Used Metal, Magnesium - A Lightweight Metal, Potassium - Another Highly Reactive Element, Sodium and Salt, Titanium - Strong but Lightweight

Refractory metals are metallic elements of the periodic table with unique properties such as extremely high melting points. However, they can remain solid at room temperature. These characteristics make these materials ideal for research-based and critical nuclear reactions. What Are Refractory Metals? Refractory metals possess a melting point above 2,000° Celsius (3,632° F) and are […]
Tags: Methods to improve the heat resistance of alloys, Molybdenum based alloys, pure metals, pure molybdenum and tungsten, Refractory alloys based on tungsten, Refractory Metal Alloys, Refractory Metals in Nuclear Reactions, Refractory Metals in Various Industries, Refractory niobium-based alloys, silicon-based coatings, TZM Niobium
Copyright © 1994-2024 Advanced Refractory Metals owned by Oceania International LLC, All Rights Reserved.