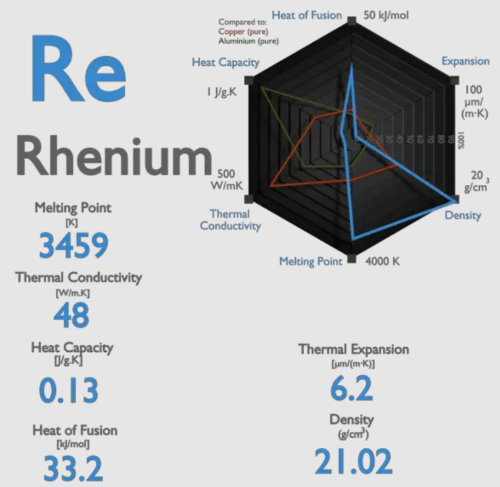
Rhenium is a silvery white element with a metallic luster. It has a high-density point exceeded only by platinum, iridium, and osmium, and its melting point is exceeded only by tungsten and carbon.
The usual commercial form of the element is powder, but it can be consolidated by pressing and resistance-sintering in a vacuum or hydrogen atmosphere.
Rhenium had good wear resistance and can withstand corrosion. Therefore, it’s commonly used as an electrical contact material. Rhenium wire is used in flash photography. It is used in the hydrogenation of fine chemicals and as an additive to tungsten and molybdenum-based alloys.
Introduction Rhenium may not be a household name, but in the world of science and industry, it stands out for its astonishingly high melting point of approximately 3,180 degrees Celsius. This often-overlooked metal plays a vital role in a wide range of applications. We’ll explore its ability to withstand extreme environments in this article. What […]
Tags: High Melting Points, Metals, rhenium

Preparation of Rhenium Powder Preparation of rhenium powder refers to the metallurgical process of producing metal rhenium powder from rhenium compounds. The rhenium compounds commonly used in the production of rhenium powder are ammonium perrhenate, potassium perrhenate, rhenium(VII) oxide, and rhenium pentachloride. The commonly used methods for the preparation of rhenium powder include hydrogen reduction, electrolysis, and […]
Tags: Advanced Refractory Metals, ARM, Electrolysis, Halide Thermal Dissociation, Hydrogen Reduction, methods for the preparation of rhenium powder, Molybdenum, molybdenum wire, refractory metals & alloys, Rhenium Compounds, rhenium metal, rhenium powder, tantalum sheets, Tungsten, tungsten wire

Properties and Compounds of Rhenium Rhenium is a silvery-white rare metal with a high melting point. Its melting point ranks third among all elements, second only to tungsten and tantalum. Because metal rhenium is hard, wear-resistant, corrosion-resistant, and stable in the air, it is widely used in aerospace, electronics, petrochemical, and other fields. In this article, let’s […]
Tags: Advanced Refractory Metals, ARM, Chemical Properties of Rhenium, Compounds of Rhenium, metal with a high melting point, Physical Properties of Rhenium, Properties and Compounds of Rhenium, Properties of Rhenium, Re2O7, ReB2, ReCl3, ReCl5, ReCl6, ReF4, ReF5, ReF6, ReF7, ReO2, ReO3, rhenium, Rhenium Compounds, rhenium metal, rhenium oxide, tantalum, Tungsten

6 Interesting Facts about Rhenium Rhenium is a rare silver-white metal and belongs to the 6th-period transition metal in the periodic table. It is one of the rarest elements in the earth’s crust and one of the highest melting and boiling elements. In today’s article, we will take a look at 6 interesting facts about rhenium. Interesting Facts […]
Tags: 6 Facts About Rhenium, 6 Interesting Facts About Rhenium, Advanced Refractory Metals, ARM, Fact About Rhenium, Facts About Rhenium, Interesting Facts About Rhenium, refractory metal products, rhenium, Rhenium Fact, Rhenium Facts, rhenium metal, The Discovery of Rhenium, The Extraction Process of Rhenium, The Properties of Rhenium, The Recycling of Rhenium, The Reserves and Production of Rhenium, The Uses of Rhenium, Transition Metal

What Can Rhenium Be Used For? Rhenium is classified as a scarce refractory metal. It has the second-highest melting point of any of the metals and has a relatively high density. Rhenium is produced as a powder from molybdenite, which also contains rhenium sulfide. The rhenium powder is consolidated by pressing and resistance sintering in […]
Tags: Advanced Refractory Metals, Refractory Metals, rhenium, Rhenium bars, rhenium powder, thermocouple alloys, What Can Rhenium Be Used For?

What Is Rhenium Metal Powder Used to Make? Only tungsten and carbon have higher melting points. Rhenium has good wear resistance and it can withstand arc corrosion. It is soluble in nitric and sulphuric acids. Applications for the metal include its use as an alloying element with tungsten. Rhenium powder is a light-gray metal powder made […]
Tags: Advanced Refractory Meatal, radiopharmacy, Refractory Metals, rhenium, Rhenium Metal Powder, rhenium powder, Tungsten, What Is Rhenium Metal Powder Used to Make?
Copyright © 1994-2024 Advanced Refractory Metals owned by Oceania International LLC, All Rights Reserved.