Molybdenum Electrodes for Glass Furnaces

Introduction
The glass manufacturing industry is boosting with a market of 106.44 billion dollars in 2021[1], and millions of tons of glass are produced every day using molybdenum electrodes and other agents. Here, we are going to focus on glass melting and the molybdenum electrodes it employs. Hope that you can have a better understanding of the requirements, types, and properties of molybdenum electrodes.

Figure 1 Molybdenum Electrodes
Glass Melting
--What Is Glass Melting?
Glass melting is the process to obtain molten glass from a mixture of raw materials at high temperatures. It is an essential part of glass manufacturing. In this process, a large amount of sand is mixed with oxides, carbonates, fluorides, etc., and they are heated at high temperatures ranging from 1500 to 1700°C. The whole process is affected by rising gases, air injections, and other elements inside the furnace. Figure 2 [2] shows the structure of a glass-melting furnace.
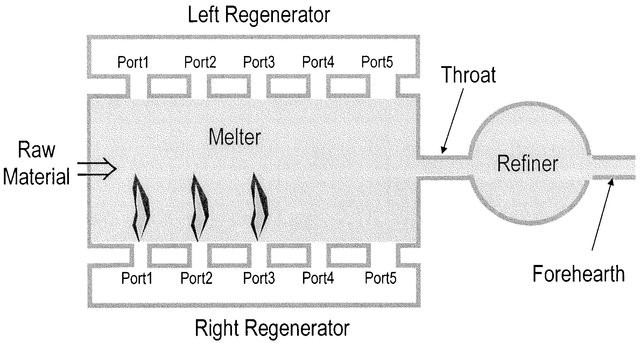
Figure 2. Birdseye Section Structure of A Glass Melting Furnace
--The Development of Glass Melting
Glass melting has developed for several years. The glass furnace has changed from gas-fired to current-powered.
Conventionally, the glass furnaces burned fossil gases and air to get energy, which was not environmentally friendly. Also, countless energy was lost because the raw materials are drawn out constantly.
Recently, the electrical heating method is widely used. This method is rather beneficial because of its lower emissions, increased melting rate, and improved energy efficiency. Electrical heating using molybdenum electrodes are on the rise, accounting for about half of the U.S.A.’s market.
Electrode Materials
--What Are Electrode Materials?
Glass-melting electrodes are important devices that are used in the glass furnace to conduct electricity and harvest energy. A majority of glass-melting electrodes are made from molybdenum. These electrodes can be graphite, pure metals, or alloys as well. Besides, remember to consider the following factors for glass melting: furnace design, electrode composition and structure, the shape of electrodes, and the number of electrodes.
--Requirements for Glass-Melting Electrodes
Glass-melting electrodes and other melting applications are supposed to withstand aggressive molten glass and maintain their impressive performance at high temperatures.
- These electrodes should have high melting points since the melting temperature of glass ranges from 1400 °C to 1600 °C.
- Glass-melting electrodes with notable thermal properties are required to stand the high-temperature environment of glass manufacturing.
- Glass-melting electrodes need great oxidation resistance, electrical conductivity, and creep resistance at elevated temperatures.
Related reading: Influence Of Molybdenum Electrodes On The Quality Of Glass Products
Molybdenum Electrodes
--What Are Molybdenum Electrodes?
Molybdenum electrodes are highly functional electrodes made from molybdenum metal. These electrodes share similar features with molybdenum metal.
Both molybdenum metal and molybdenum electrodes are strong materials with great thermal properties. Molybdenum is a hard silvery metal with a Mohs hardness of 5.5. Additionally, it has a melting point of 2,623 °C (4,753 °F), which is only second to tantalum, tungsten, and carbon. Molybdenum does not react with oxygen or water at room temperature as well.
Thus, nearly 95% of glass-melting electrodes are made from molybdenum thanks to its high hardness and high melting point.
--Benefits of Molybdenum Electrodes
Molybdenum electrodes meet the requirements of glass-melting electrodes in the following aspects.
- High Melting Point: Glass-melting electrodes should stand high temperature since the working temperature in the glass furnace is quite higher. Molybdenum and tungsten are suitable materials. However, Tungsten is much more expensive and hard to work on.
- Great Thermal Properties: Molybdenum has high electrical and thermal conductivity, a low coefficient of expansion, and remarkable thermal shock resistance.
- Corrosion Resistance: High-purity molybdenum has good corrosion resistance, so they are used to extend the life of glass furnaces.
- Creep Resistance: Molybdenum has great creep strength after the temperature exceeds 1300℃. Platinum shows toughness at relatively low temperatures, yet it is easily broken at high temperatures.
Related reading: Application Of Molybdenum In The Glass Industry
Conclusion
Molybdenum electrodes are commonly used for glass melting because of their high melting point, notable thermal and electrical conductivity, and high strength. Advanced Refractory Metals (ACM) is a leading supplier of molybdenum electrodes of different sizes. Please check our website for more information.
Reference:
[1] Glass View Research. (2017 - 2020). Glass Manufacturing Market Size, Share & Trends Analysis Report By Product (Container, Flat, Fiber), By Application (Packaging, Construction), By Region, And Segment Forecasts, 2022 - 2030. https://www.grandviewresearch.com/industry-analysis/glass-manufacturing-market
[2] Moon, Un-Chul & Lee, K.Y.. (2003). Hybrid Algorithm with Fuzzy System and Conventional PI Control of TV Glass Furnace. Control Systems Technology, IEEE Transactions on. 11. 548 - 554. 10.1109/TCST.2003.813385.
{{item.content}}
LEVE A REPLY
{{item.children[0].content}}
{{item.content}}






