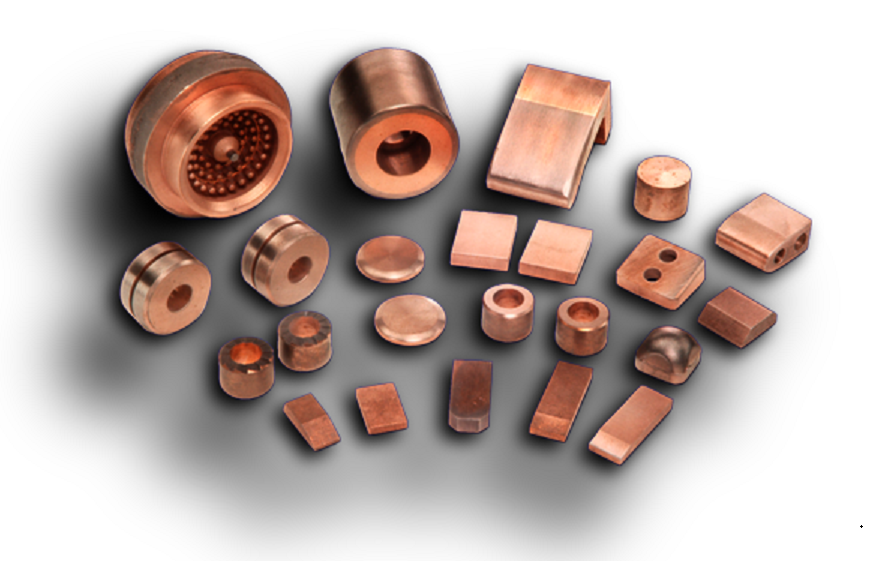

In this article, we’ll take a look at the main applications of tungsten-copper composites (W-Cu composites). Since tungsten (W) has good electron emission function, a class of composites such as tungsten alloy and W-Cu is good electrode materials, which have been widely used in EDM, electric locomotive guide block, ultra-high voltage switch, and welding in the electric power industry.

Main Applications of Tungsten-copper Composites (W-Cu Composites)
The tungsten-rhenium alloy has replaced platinum as a temperature thermocouple on many occasions, and the high-performance tungsten-rhenium wire is also used as the electron material for display tube launching into thousands of households. Moreover, chromium, vanadium, and other materials have been widely used in electron microscopy and coated glass.
Tungsten has a high hardness and the highest melting point among all metals. Copper (Cu) has excellent electrical and thermal conductivity, while the W-Cu composites have good electrical and thermal conductivity, low thermal expansion coefficient, and high resistance to arc corrosion, so they have been widely used as electric contacts, EDM, resistance welding, and plasma electrode materials for a long time.
With the development of microelectronic information technology, W-Cu composite material has been widely used in large-scale integrated circuits and high-power microwave devices.
W-Cu composite
Due to the melting point of W (3390 ~ 3430 ℃) being much higher than the boiling point of Cu (2350 ~ 2600 ℃), the Cu in tungsten-copper can cool down and maintain the integrity of the tungsten skeleton through “sweat” heat dissipation under the action of high-temperature arc when used as an electric contact, thus ensuring the good breaking function of the electric contact.
The W-Cu composite material has excellent resistance to arc corrosion, fusion welding, and voltage resistance, making it especially suitable for use as high voltage and UHV open and close contacts, such as in vacuum switch appliances and new high voltage appliances with SF6 as arc extinguishing medium.
With the rapid development of IC chip technology, the requirement for IC packaging materials is more and more demanding. In addition to the requirement that electronic packaging materials have thermal conductivity (TC) of up to 170 ~ 190 W/(m•K) and low and specially set coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE), they also need to be easy to process and shape with low cost.
The W-Cu composite material makes it easy to adjust the thermophysical parameters and greatly improves its application range in microelectronic devices. Therefore, it is regarded as a good heat sink material in high-power devices. The suitable thermal expansion coefficient can be well-matched with semiconductor materials such as silicon chips, gallium arsenide, and ceramic materials in microelectronic devices, thus avoiding thermal fatigue damage caused by thermal stress.
Besides that, the W-Cu composite material can also be formed in the final size, and the device can be miniaturized.

electronic packaging
The development of various advanced electro-machining technologies has also become another important application field of W-Cu composites with high heat resistance, high electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, and arc ablation resistance.
Cu and Cu alloy are widely used as machining electrodes during the long period of EDM. Although Cu and copper alloy are cheap and convenient to use, the electrode material consumption is too large and the machining accuracy is poor due to the fact that Cu and copper alloy electrodes are not resistant to EDM erosion. Therefore, it cannot meet the needs of special machining on many occasions.
Thank you for reading our articles and we hope it can be helpful to you. If you want to know more about the applications of tungsten-copper composites (W-Cu composites), you can visit Stanford Advanced Materials for more information. They supply high-quality tungsten products to meet customers’ R&D and production needs.
Copyright © 1994-2024 Advanced Refractory Metals owned by Oceania International LLC, All Rights Reserved.