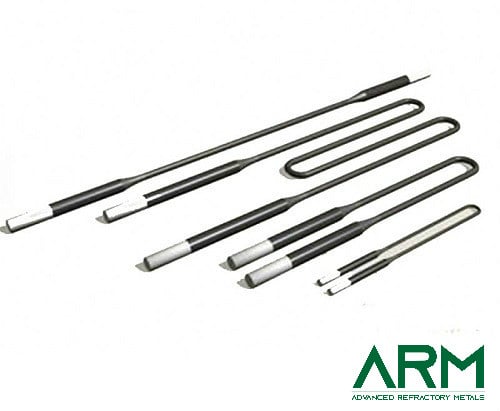
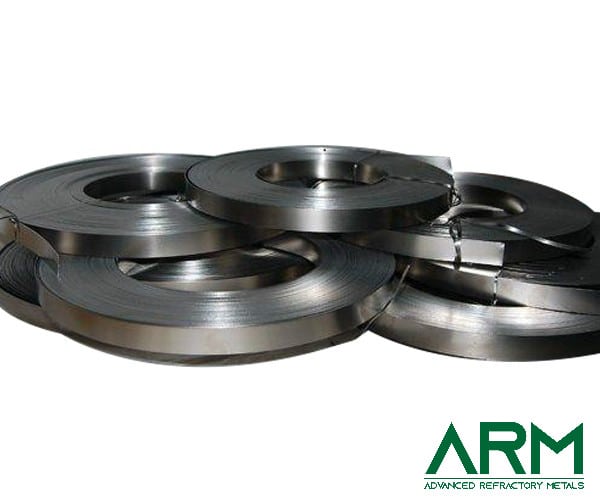
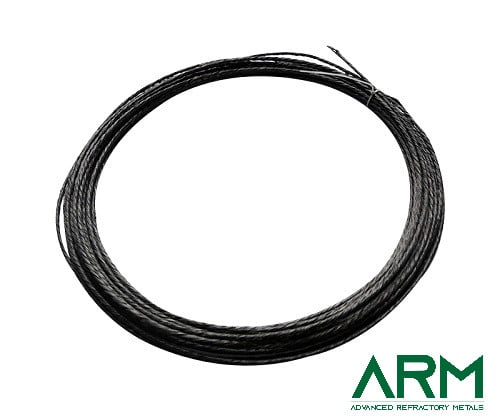
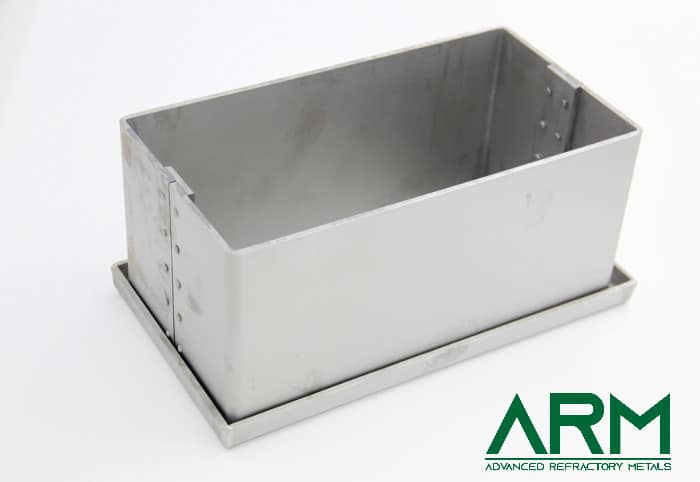
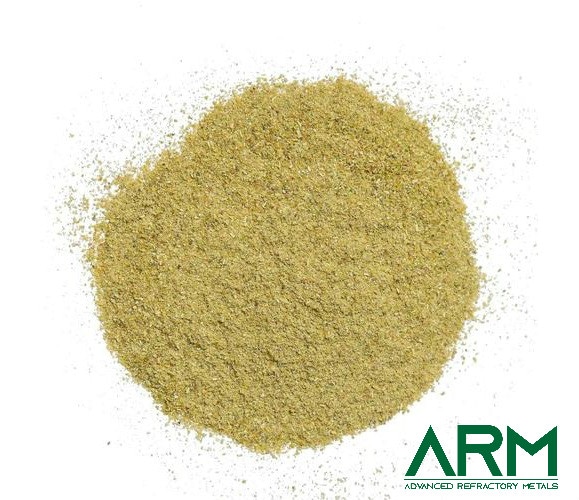
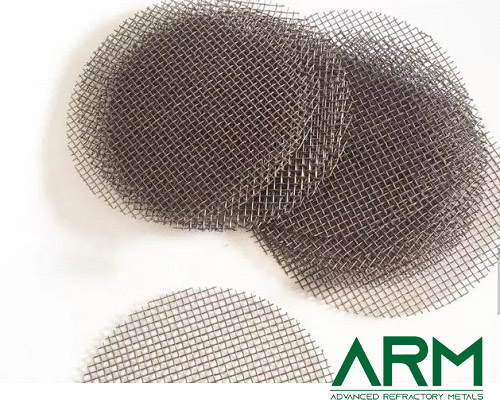
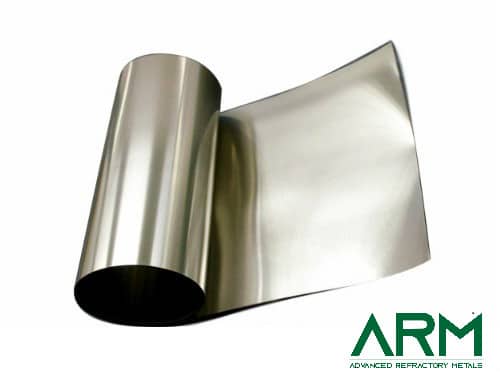
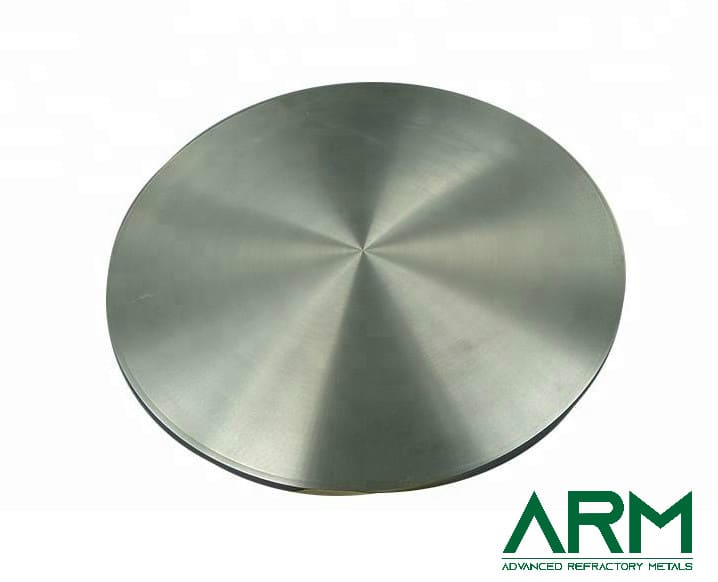
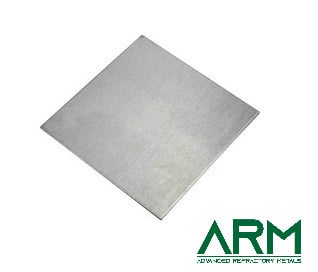
TZM0092 TZM Alloy (TZM Molybdenum)
TZM alloy (Titanium-Zirconium-Molybdenum) is an alloy of 0.50% Titanium, 0.08% Zirconium and 0.02% Carbon with the balance molybdenum. TZM Molybdenum has a higher recrystallization temperature, higher strength, hardness and good ductility at room and elevated temperatures than unalloyed Molybdenum.
Descriptions of TZM Alloy (TZM Molybdenum)
TZM alloy (Titanium-Zirconium-Molybdenum) is an alloy of 0.50% Titanium, 0.08% Zirconium and 0.02% Carbon with the balance molybdenum. TZM Molybdenum has a higher recrystallization temperature, higher strength, hardness and good ductility at room and elevated temperatures than unalloyed Molybdenum.
Advanced Refractory Metals is a trusted supplier and manufacturer of pure molybdenum and molybdenum alloys. Various forms and dimensions are available.
Specifications of TZM Alloy (TZM Molybdenum)
|
Form |
Size (mm) |
Process |
Surface |
|
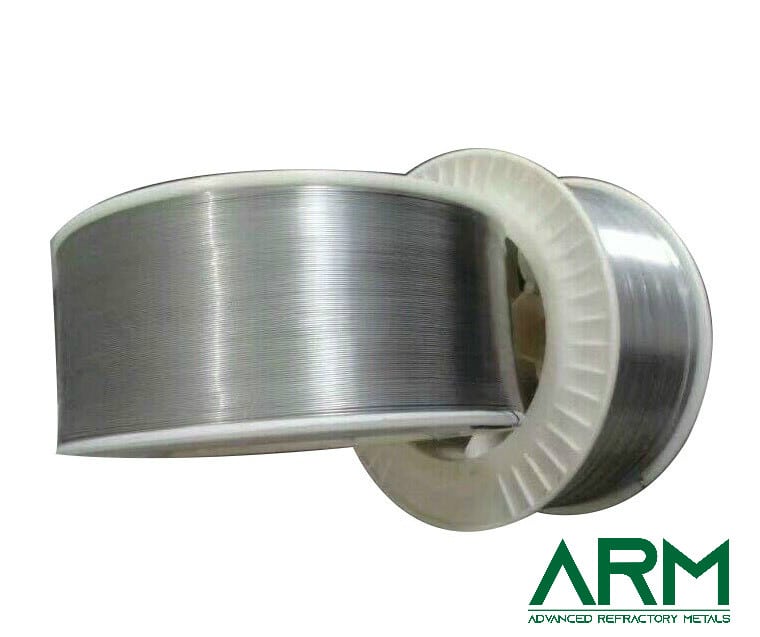
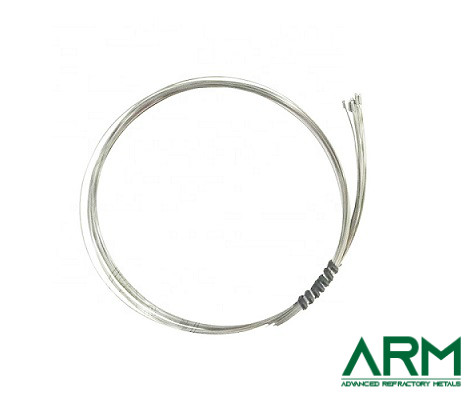
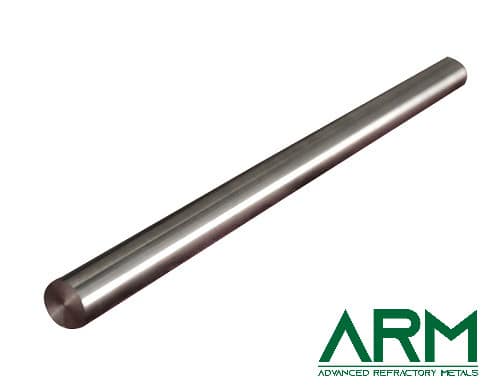
Wire (straight or rolled) |
Dia.: 0.5-4.0 Length: Customized |
- |
Black oxide; Chemically cleaned |
|
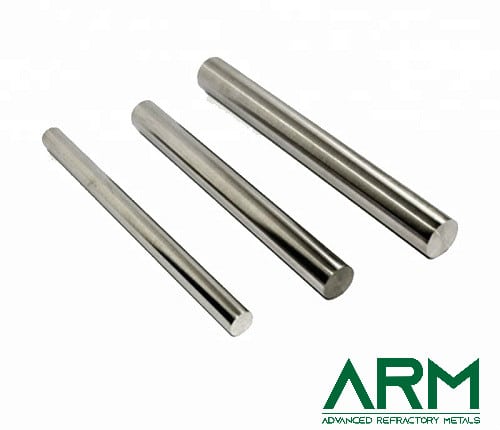
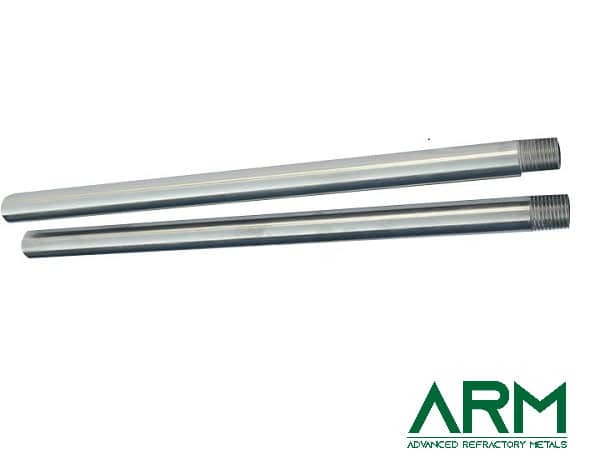
Rod |
Dia.: 4.0-100 Length: <2000 |
Drawing; swaging |
Black oxide; Chemically cleaned; Grinding |
|
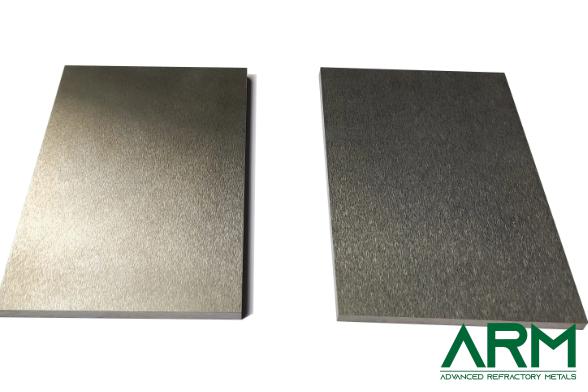
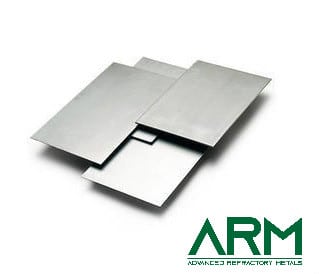
Plate |
Thickness: 4.75-50 Width: Customized Length: Customized |
Forging; rolling |
Chemically cleaned; Grinding |
|
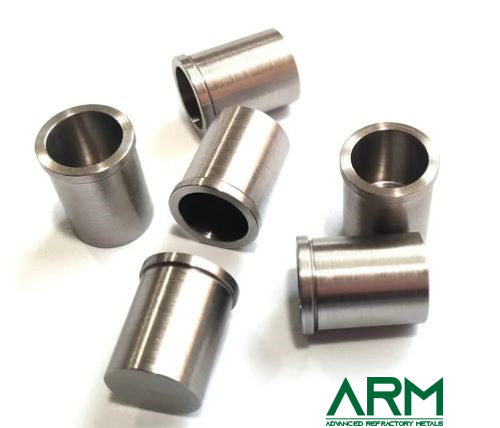
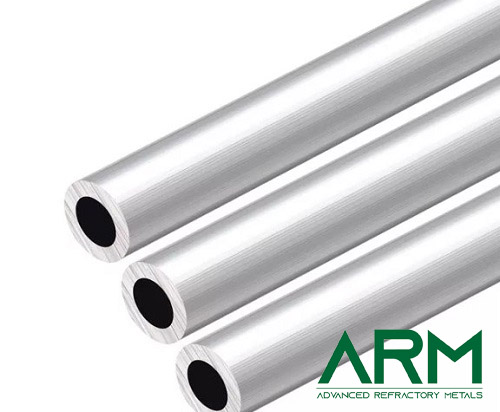
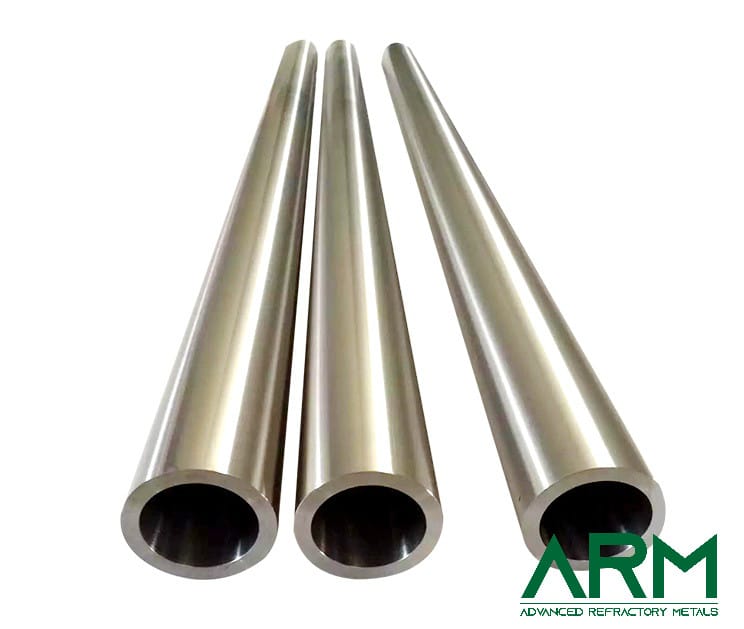
Tube |
O.D.: 0.8"-20" Length: Customized |
Sintering; drilling |
Fine Turning; Grinding |
* Properties of TZM alloy
| Material | Density(g/cm3) | Melting Point(℃ ) | Boiling Point(℃ ) |
| TZM | 10.22 | 2617 | 4612 |
* Mechanical properties of TZM alloy
| Mechanical properties | Elongation/% | Modulus elasticity/GPa | Yield strength/MPa | Tensile strength /MPa |
Fracture toughness /(MPa·m1/2 |
| Data | <20 | 320 | 560-1150 | 685 | 5.8-29.6 |
* Thermal and electrical properties of TZM alloys
| Properties | The coefficient of thermal expansion/K-1 (20~100℃) |
Thermal conductivity W /m·K | Working temperature/℃ | Resistivity/Ω·m |
| Data | 5. 3×10-6 | 126 | 400 | (5. 3~5. 5)×10-8 |
Applications of TZM Alloy (TZM Molybdenum)
-
Aerospace Components: TZM alloy is extensively used in rocket engine nozzles and re-entry vehicle heat shields due to its ability to maintain structural integrity at extreme temperatures up to 1,600°C.
-
High-Temperature Furnace Systems: TZM alloy serves as critical heating elements, radiation shields, and support structures in industrial furnaces, leveraging its exceptional melting point of ~2,620°C.
-
Glass Manufacturing Equipment: TZM alloy is the material of choice for glass melting electrodes, stirrers, and forming molds, where its thermal stability prevents contamination and deformation.
-
Nuclear Reactor Components: TZM alloy is utilized in reactor core components and fuel cladding, benefiting from its neutron absorption properties and radiation resistance.
-
Metal Forming Tools: TZM alloy is employed in die-casting molds, extrusion dies, and hot-work tooling, where its high-temperature strength and wear resistance significantly extend tool life.
-
Semiconductor Industry: TZM alloy finds application in high-temperature processing equipment for silicon wafer production, thanks to its thermal conductivity and vacuum compatibility.
Packaging of TZM Alloy (TZM Molybdenum)
Our TZM alloys are wrapped in foam and packaged in plywood cases to ensure safe storage and transportation.
FAQs
Q1. How does TZM alloy differ from pure molybdenum?
- Composition:
- Pure Mo: 99.95% molybdenum
- TZM: Mo + 0.5% Ti + 0.1% Zr (enhances strength and creep resistance)
- Performance:
- High-temp strength: TZM retains 2× higher strength above 1,300°C.
- Creep resistance: Superior under prolonged heat/stress.
- Recrystallization temp: TZM (~1,100°C) > Pure Mo (~900°C).
Q2. What’s the working temperature range of TZM?
- Optimal range: 700–1,400°C (in vacuum/inert gas).
- Oxidation: Begins at 400°C; rapid above 500°C (requires protective coatings).
- Strength comparison:
- Room temp: Similar to pure Mo.
- >1,300°C: Twice as strong as pure Mo.
Q3. Key applications of TZM alloy?
1. Aerospace/Defense: Rocket nozzles, heat shields.
2. Industrial Furnaces: Heating elements, crucibles.
3. Nuclear/Energy: Reactor components, plasma-facing parts.
4. Electronics: Heat sinks, semiconductor tools.
Related reading:
Titanium Zirconium Molybdenum (TZM) Alloy For Hot Runner Nozzles
TZM Alloy Applications, Properties & Preparation Methods- Your Name (required)
- Your Email (required)
- Company Name (required)
-
Country (required)
United States
- United States
- Afghanistan
- Aland Islands
- Albania
- Algeria
- American Samoa
- Andorra
- Angola
- Anguilla
- Antarctica
- Antigua and Barbuda
- Argentina
- Armenia
- Aruba
- Australia
- Austria
- Azerbaijan
- Bahamas
- Bahrain
- Bangladesh
- Barbados
- Belarus
- Belgium
- Belize
- Benin
- Bermuda
- Bhutan
- Bolivia
- Bosnia and Herzegovina
- Botswana
- Bouvet Island
- Brazil
- British Indian Ocean Territory
- British Virgin Islands
- Brunei
- Bulgaria
- Burkina Faso
- Burundi
- Cambodia
- Cameroon
- Canada
- Cape Verde
- Cayman Islands
- Central African Republic
- Chad
- Chile
- China
- Christmas Island
- Cocos (Keeling) Islands
- Colombia
- Comoros
- Congo
- Cook Islands
- Costa Rica
- Croatia
- Cuba
- Cyprus
- Czech Republic
- Democratic Republic of Congo
- Denmark
- Disputed Territory
- Djibouti
- Dominica
- Dominican Republic
- East Timor
- Ecuador
- Egypt
- El Salvador
- Equatorial Guinea
- Eritrea
- Estonia
- Ethiopia
- Falkland Islands
- Faroe Islands
- Federated States of Micronesia
- Fiji
- Finland
- France
- French Guyana
- French Polynesia
- French Southern Territories
- Gabon
- Gambia
- Georgia
- Germany
- Ghana
- Gibraltar
- Greece
- Greenland
- Grenada
- Guadeloupe
- Guam
- Guatemala
- Guinea
- Guinea-Bissau
- Guyana
- Haiti
- Heard Island and Mcdonald Islands
- Honduras
- Hong Kong
- Hungary
- Iceland
- India
- Indonesia
- Iran
- Iraq
- Iraq-Saudi Arabia Neutral Zone
- Ireland
- Israel
- Italy
- Ivory Coast
- Jamaica
- Japan
- Jordan
- Kazakhstan
- Kenya
- Kiribati
- Kuwait
- Kyrgyzstan
- Laos
- Latvia
- Lebanon
- Lesotho
- Liberia
- Libya
- Liechtenstein
- Lithuania
- Luxembourg
- Macau
- Macedonia
- Madagascar
- Malawi
- Malaysia
- Maldives
- Mali
- Malta
- Marshall Islands
- Martinique
- Mauritania
- Mauritius
- Mayotte
- Mexico
- Moldova
- Monaco
- Mongolia
- Montenegro
- Montserrat
- Morocco
- Mozambique
- Myanmar
- Namibia
- Nauru
- Nepal
- Netherlands Antilles
- Netherlands
- New Caledonia
- New Zealand
- Nicaragua
- Niger
- Nigeria
- Niue
- Norfolk Island
- North Korea
- Northern Mariana Islands
- Norway
- Oman
- Pakistan
- Palau
- Palestinian Territories
- Panama
- Papua New Guinea
- Paraguay
- Peru
- Philippines
- Pitcairn Islands
- Poland
- Portugal
- Puerto Rico
- Qatar
- Reunion
- Romania
- Russia
- Rwanda
- Saint Helena and Dependencies
- Saint Kitts and Nevis
- Saint Lucia
- Saint Pierre and Miquelon
- Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
- Samoa
- San Marino
- Sao Tome and Principe
- Saudi Arabia
- Senegal
- Serbia
- Seychelles
- Sierra Leone
- Singapore
- Slovakia
- Slovenia
- Solomon Islands
- Somalia
- South Africa
- South Georgia and South Sandwich Islands
- South Korea
- Spain
- Spratly Islands
- Sri Lanka
- Sudan
- Suriname
- Svalbard and Jan Mayen
- Swaziland
- Sweden
- Switzerland
- Syria
- Taiwan
- Tajikistan
- Tanzania
- Thailand
- Togo
- Tokelau
- Tonga
- Trinidad and Tobago
- Tunisia
- Turkey
- Turkmenistan
- Turks And Caicos Islands
- Tuvalu
- US Virgin Islands
- Uganda
- Ukraine
- United Arab Emirates
- United Kingdom
- United States
- United States Minor Outlying Islands
- Uruguay
- Uzbekistan
- Vanuatu
- Vatican City
- Venezuela
- Vietnam
- Wallis and Futuna
- Western Sahara
- Yemen
- Zambia
- Zimbabwe
- Your Phone (Optional)
-
Metals (Optional)
Tantalum...
-
I would like to join the mailing list to receive updates from Advanced Refractory Metals.
- Notes (required)
-
Attachment (Optional)
No file chosen
-