The Use of Tungsten Powder in Cathodes for Electron Tubes and X-ray Tubes
Tungsten, with its high melting point, excellent conductivity, and density, has long been a material of choice for high-performance applications. One of the most critical uses is in the manufacturing of cathodes for electron tubes and X-ray tubes. Let's explore how tungsten powder is used in cathodes for electron tubes and X-ray tubes and why it's such a vital component in these technologies.

[1]
Definition of Electron Tube
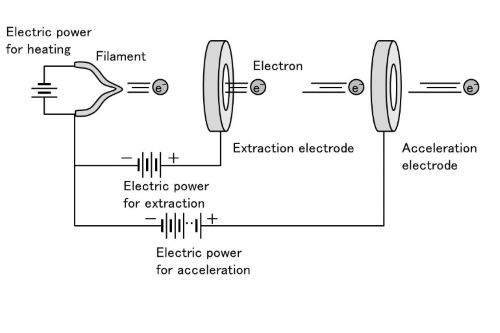
An electron tube, also known as a vacuum tube or thermionic tube, is essentially an electron conveyance device used for controlling the flow of electrons inside a vacuum between electrodes. They are used as electron conveyance components in devices such as radio transmission systems, television systems, radar systems, and medical instruments such as X-ray machines.
The primary purpose of the electron tube is to create a stream of electrons from a heated cathode to a positively charged anode (anode is the target where the collision of the electrons will produce X-rays) in a vacuum or a low-pressure gas. The cathode is the most important part of the electron tube, which provides the necessary electrons to create the flow of electrons. In the X-ray tube, the cathode provides the electrons that would later collide to produce X-rays.
Why Tungsten Powder for Cathodes?
The application of tungsten powder in cathodes for electron tubes or X-ray tubes can be considered based on certain properties of tungsten, which are essential for the performance of tubes:
1. High Melting Point
One of the remarkable qualities of tungsten is the high melting point of 3,422 °C (6,192 °F). This is the highest of all metals and makes tungsten highly suitable for use in high-temperature conditions. In electron tubes, the cathode needs to be heated in order to emit electrons, a phenomenon known as thermionic emission.
Within the X-ray tubes, the cathode experiences cyclic processes involving constant heating and cooling cycles, since the cathode emits electrons, which ultimately hit the anode. Tungsten's resistance to the above thermal stresses ensures the component functions properly without failing due to overheating.
2. Thermionic Emission Properties
Thermionic emission is a process that involves electron emission from a heated material. The melting point of tungsten is very high, as well as its efficiency in electron emission, which makes it a suitable material for such a job. The heating of the cathode results in the emission of electrons from the tungsten atoms, which then form an electron flow that is needed for the process to proceed to the anode.
The value for the work function for tungsten is quite low compared to other elements, making it easier to emit electrons, hence improving the efficiency of the electron tube. The efficiency of electron emission is very important for the functionality of an X-ray tube because the process of emitting electrons should happen very fast to produce quality X-rays.
3. Durability and Longevity
Electron tubes or X-ray tubes function in extreme conditions. For the cathode in these tubes, it is not only required to have high electron emissivity but also be able to withstand the constant current heating. A high thermal conductivity in tungsten ensures that the heating is evenly dispersed, which could otherwise result in the decomposition of the material of the cathode.
Additionally, tungsten is very strong and resilient, hence quite durable, and this is really important to keep the longevity of the cathode. The tungsten cathodes bear mechanical stresses and constant electron bombardment without deterioration; hence, they are extremely reliable both in electron tubes and X-ray tubes.
4. Electron Emission and Stability
In the case of using tungsten in powder form, it can be processed to result in a fine, porous structure with enhanced electron emission. Its surface area increases to get more efficient electron release. Fine powders are very common in use for cathode production because they improve a lot the possibility to emit a stable and regular flow of electrons-the target of every high-performance electron tube and even an X-ray tube.
Also, the porosity and structure of tungsten powder support the emitted electrons so that they do not lose their energy prematurely, thus further optimizing performance for the cathode.
5. Compatibility with X-Ray Tubes
In X-ray tubes, the cathode not only needs to provide the emission of electrons but also be capable of resisting a large voltage difference, which is a significant parameter to create X-rays. The heavy electrical conductivity of tungsten helps provide a focused flow of the emitted electrons to the anode. The interaction of the electrons with the target anode results in the creation of X-rays, which are emitted at the object to be imaged.
Tungsten also has an important role in preventing overheating of the tube during the process of generation of the X-ray. This element has the ability to absorb and dissipate heat effectively in order to ensure that the X-ray tube operates in appropriate conditions.
Tungsten Powder Used in Making the Cathode
The application of tungsten powder is largely used in preparing cathodes for electron and X-ray tubes, a process known as sintering. The preparation involves compacting the tungsten powder into a certain shape, presumably that of a filament, before subjecting it to certain temperatures in a vacuum environment as a final process.
This enables the tungsten powder to preserve its specific properties while still being able to provide the required physical strength to act as a cathode in an electron tube or an X-ray tube.
The particle size and purity of the tungsten powder are important factors in determining the quality of the cathodes. The powder should have no contaminants to retain its thermionic emission characteristics.
Uses of Tungsten Cathodes
1. Medical X-ray Tubes
Medical X-ray tubes are highly dependent on tungsten-cathode electron emitters. In the process, the tungsten cathode gives off electrons that collide with a tungsten anode, leading to the production of X-rays. These X-rays are vital in medical imaging, allowing doctors to perform accurate diagnoses. Tungsten usage is significant in influencing the quality of X-ray production in medical imaging.
It particularly affects the effectiveness of diagnostic imaging.
2. Industrial X-Ray Tubes
Besides medical imaging, X-ray tubes can be found in some industrial applications, for instance, non-destructive testing, where the X-ray tube is applied to examine the internal structure of materials and products. In such instances, X-ray tubes with tungsten powder cathodes aid the production of high-quality X-rays essential for material flaw detection.
3. Electron Tubes in Telecommunication and Electronics
Electron tubes, which encompass devices such as oscilloscopes and signal amplifiers, employ the use of tungsten cathodes to ensure efficient emission of electrons. The steady and reliable flow of electrons is necessary in all aspects pertaining to communication to scientific research. The use of tungsten ensures that these electron tubes last for a long while.
Related reading: 3 Primary Uses of Tungsten
Conclusion
The use of tungsten powder in cathodes for electron tubes and X-ray tubes is a critical advancement that supports numerous high-performance applications. With its high melting point, excellent thermionic emission properties, durability, and ability to withstand extreme conditions, tungsten plays an indispensable role in ensuring the efficiency and longevity of these devices. For more tungsten products, please check Advanced Refractory Metals (ARM).
Reference:
[1] Naoaki, Fukuda & Toshio, Takiya & Min, Han. (2018). Properties of Quantum Beams and Their Applications. Applied Physics Research. 10. 30-30. 10.5539/apr.v10n2p30.
{{item.content}}
LEVE A REPLY
{{item.children[0].content}}
{{item.content}}






