Tantalum Capacitors: A Comprehensive Guide

1. Introduction
Tantalum capacitors or tantalum electrolytic capacitors are a very specialized capacitor using metallic tantalum as the dielectric. First developed in 1956 by Bell Labs, they are found to have excellent performance characteristics with minimal size and maximum capacitance. The unique properties of tantalum make it an extremely efficient capacitor material with high efficiency in a small body.
These capacitors have extensive use in a wide range of applications like military communication, aerospace technology, and industrial control. The usability of tantalum capacitors extends to consumer electronics, film machines, and communications equipment, where they are of extreme importance for performance and reliability.

2. Basic Structure
A typical tantalum capacitor consists of a metal anode made of high-purity tantalum, a dielectric oxide layer, and a cathode. The dielectric layer is achieved by oxidizing the surface of the tantalum metal, and it is this that provides the capacitor with high capacitance and stability. The casing is often made of a solid or a wet electrolyte, and the polarity of the capacitor is indicated by leads or markings.
Tantalum capacitors are mostly manufactured in wet or solid form. Solid tantalum capacitors are generally applied due to their compactness and reliability, while wet tantalum capacitors having a liquid electrolyte are traditionally applied for use in high voltages.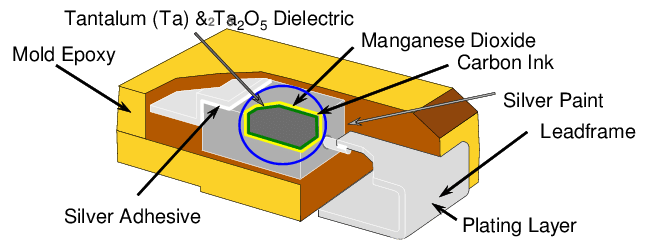 [1]
[1]
3. Production Process
Production of tantalum capacitors encompasses certain key steps which contribute notably towards the end-product performance and quality. The simple list of manufacturing steps comprises:
• Preparation of Tantalum Powder: The starting material is high-purity tantalum powder.
• Molding and Pressing: The powder is pressed into small cylindrical shapes, which will form the anode of the capacitor.
• Oxidation: The tantalum is then subjected to a high-voltage oxidation process, producing a thin insulating oxide layer that will form the dielectric material.
• Electrolyte Application: A conductive electrolyte is deposited to form the cathode.
•Sealing and Testing: After assembly, the capacitor is sealed and subjected to rigorous testing to ensure it meets the established parameters of capacitance, voltage, and leakage.
All these operations are crucial in ensuring the resulting product possesses the required performance characteristics, e.g., long life, high capacitance, and stability under different conditions.
4. Key Performance Parameters
Tantalum capacitors are characterized by a list of performance characteristics that define their application in an application:
•Capacitance Value: Tantalum capacitors possess high capacitance values compared to their size, thus being suitable for applications with limited space.
•Voltage Rating: Voltage rating defines the maximum voltage that the capacitor can handle. It will be destroyed if a voltage higher than this is applied.
•ESR (Equivalent Series Resistance): The capacitors require low ESR for high-frequency applications and low heat generation.
•Leakage Current: It is an indication of the current that leaks through the dielectric when the capacitor is in operation, and less leakage current is preferred for stability.
•Temperature Stability: The capacitors have superior performance within a wide temperature range, which is extremely important in industrial and automotive applications.
As a reliable supplier, Advanced Refractory Metals (ARM) offers tantalum capacitors with the following specifications:
|
Product No. |
Chemical Compositions (ppm) |
Physical Properties |
Electrical Properties |
|||
|
Impurities ≤ |
SBD |
Fsss |
Capacitance |
Dc Leakage |
||
|
O |
N |
|||||
|
TaA001 |
1800 |
100 |
1.9-2.5 |
4.5-7.5 |
6000+10 -5% |
<2.0×10-4 |
|
TaA002 |
2200 |
120 |
1.8-2.3 |
4.5-6.5 |
8000+10 -5% |
<2.0×10-4 |
|
TaA003 |
2400 |
150 |
1.7-2.1 |
2.5-4.5 |
15000+10 -5% |
<2.2×10-4 |
|
TaA004 |
1800 |
150 |
1.6-2.0 |
2.4-3.5 |
23000+10 -5% |
<2.2×10-4 |
|
TaA005 |
2300 |
400 |
1.7-2.1 |
2.4-3.5 |
32000+10 -5% |
<2.5×10-4 |
|
TaA006 |
2500 |
400 |
1.6-2.0 |
2.0-3.5 |
40000+10 -5% |
<2.5×10-4 |
|
TaA007 |
3200 |
400 |
1.6-2.0 |
2.0-3.4 |
50000+10 -5% |
<2.5×10-4 |
|
TaA008 |
3600 |
600 |
1.5-1.9 |
1.8-3.0 |
70000+10 -5% |
<2.8×10-4 |
|
TaA009 |
5000 |
1500 |
1.5-1.9 |
1.4-2.8 |
80000+10 -5% |
<3.1×10-4 |
|
TaA010 |
6000 |
1500 |
1.4-2.3 |
1.2-2.6 |
100000+5 -5% |
<3.5×10-4 |
|
TaA011 |
7500 |
1800 |
1.7-1.9 |
0.8-2.2 |
120000+5 -5% |
<3.5×10-4 |
|
TaA012 |
8500 |
2500 |
1.4-2.0 |
1.1-2.3 |
150000+5 -5% |
<3.5×10-4 |
|
TaA013 |
9500 |
2700 |
1.68-1.98 |
1.6-2.8 |
170000+5 -5% |
<4.0×10-4 |
|
TaA014 |
11500 |
3000 |
1.6-2.1 |
1.0-2.6 |
200000+5 -5% |
<4.5×10-4 |
5. Advantages and Disadvantages of Tantalum Capacitors
Advantages involve:
• Compact High Capacitance: Tantalum capacitors may possess high capacitance value in a very small package, which is very beneficial in compact devices.
• Reliable Performance: Tantalum capacitors provide stable performance with respect to time and with varying environmental conditions.
• Long Operating Life: These capacitors possess a long operating life when used within set limits.
• Low ESR: Due to the low ESR, tantalum capacitors can be used in applications at high frequency, such as power supplies and RF applications.
Limitations include:
• Polarized: Tantalum capacitors are polarized, i.e., they need to be correctly inserted in the circuit (positive to positive, negative to negative). If they are not so inserted, capacitor failure, including possible leakage or explosion, might occur.
•Cost: Because of the expense of the tantalum metal, these capacitors are more costly than other capacitors, like aluminum electrolytic capacitors.
•Failure Mode: Tantalum capacitors differ from other capacitors in that they can fail catastrophically if exposed to conditions beyond their rated specifications, like reverse voltage or overcurrent.
Further reading: What are the Differences Between Electrolytic, Tantalum, And Ceramic Capacitors?
6. Applications and Precautions
Tantalum capacitors have applications in a variety of areas:
•Power Supply Smoothing and Filtering: They are generally used in power supply circuits for filtering and smoothing due to their stable behavior and low ESR.
•Energy Storage and Power Conversion: Tantalum capacitors can efficiently store and provide energy and are thus ideally appropriate for use in power conversion and energy storage circuits.
•Signal Decoupling and Coupling: They are used for coupling and decoupling signals in electronic circuits to prevent interference.
• Timing Circuits: Where proper time constant performance is required in the circuits, tantalum capacitors are extensively utilized.
However, since they are polarized, one has to exercise extra caution while installing in order to properly insert the capacitor in the correct direction. Furthermore, the following precautions should be employed:
1. Correct Polarity: Ensure the positive and negative terminals are correctly labeled and connected. If not, wrong polarity may result in leakage, short-circuiting, or even explosion.
2. Voltage Rating: Do not use more than the rated voltage of the capacitor. Failure may result due to over-voltage.
3. Avoid Quick Charging/Discharging: For avoiding inrush currents that are too high, it is recommended to include a current-limited resistor in circuits where quick charging or discharging occurs.
4. Operating Temperature: Use the capacitor within its operating temperature range to avoid degradation or failure of performance.
Conclusion
Tantalum capacitors are extremely reliable components in today's electronics. They possess high capacitance in a small body. Their high-end capabilities coupled with their longevity place them at a premium in the military, aerospace, industrial, and consumer market. However, care, accurate orientation, and compliance with voltages are indispensable in a bid to guarantee their lifespan and minimize potential risks. With proper precautions, tantalum capacitors serve valuable assistance for a variety of electronic uses.
Reference:
[1] Hahn, Randy & Tempel, Kristin. (2015). Solid Electrolytic Capacitors Designed for High Temperature Applications. Additional Conferences (Device Packaging, HiTEC, HiTEN, & CICMT). 2015. 000142-000152. 10.4071/HiTEN-Session4-Paper4_4.
{{item.content}}
LEVE A REPLY
{{item.children[0].content}}
{{item.content}}






