How Nitinol Is Applied to Soft Robotics and Actuation Systems
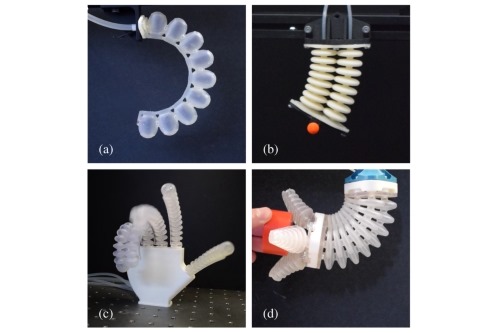
In the rapidly advancing field of soft robotics, the integration of smart materials has opened new possibilities for creating highly flexible, adaptable systems that can mimic biological processes. One such material that has garnered significant attention is Nitinol, a unique alloy of nickel and titanium.
 [1]
[1]
Artificial Muscles for Soft Robotics
One of the most compelling applications of Nitinol in soft robotics is the development of artificial muscles. Unlike traditional motors or actuators that rely on rigid components, Nitinol-based actuators can bend, stretch, and compress in ways that closely mimic biological muscles. When an electrical current is passed through the Nitinol wire or fiber, it heats up and contracts, allowing it to perform motion similar to muscle contraction. Once the current is turned off, the material cools down and returns to its original shape.
These artificial muscles offer several advantages over traditional robotic actuators. First, Nitinol actuators are highly flexible and lightweight, making them ideal for soft robotics applications where dexterity and subtle movements are required. Furthermore, their low power consumption and compact size make them particularly suitable for portable and wearable devices.
For instance, in micro-manipulation or surgical tools, microscale grippers made from Nitinol can perform delicate tasks with precision, mimicking the dexterity of human fingers. These grippers can bend and extend to grasp small objects, providing a non-invasive, highly flexible solution for tasks that require fine control, such as in microsurgery.
Wearable Robotics for Rehabilitation and Human Augmentation
Another area where Nitinol's capabilities are being leveraged is in the development of wearable robotics. These devices, which are used for rehabilitation or human augmentation, are designed to assist individuals with limited mobility or strength. Nitinol's shape memory effect allows for the creation of soft, flexible exoskeletons and wearable assistive devices that are both lightweight and unobtrusive.
In rehabilitation settings, Nitinol-based wearable robots can help patients regain mobility by providing them with the necessary support to perform everyday tasks. For example, soft robotics exoskeletons made from Nitinol can aid in walking by providing gentle, flexible support that moves with the user's natural gait. The advantage of using Nitinol in these applications is that the actuators can be powered by a small, portable battery, enabling patients to wear the device without feeling encumbered.
Moreover, Nitinol's versatility also extends to human augmentation—enhancing human capabilities. In prosthetics, for example, Nitinol actuators can be used to create highly dynamic, functional prosthetic limbs that offer a wide range of motion. Unlike traditional mechanical prosthetics, which can be heavy and restrictive, Nitinol-based prosthetics are lightweight and provide smoother, more natural movement.
Bioinspired Systems and Muscle Contraction Mimicry
In soft robotics, there is also a significant focus on creating bioinspired systems—robots that emulate the behaviors of living organisms. Nitinol plays a crucial role in this area by mimicking muscle contraction and relaxation. This biomimicry can be seen in a variety of applications, from soft robots that crawl like worms or grippers that mimic the action of a human hand, to complex systems that simulate the movement of muscles and tendons.
One notable example is the development of bioinspired soft robots that utilize Nitinol as their actuators. These robots can exhibit behaviors such as bending, twisting, and extending, much like a natural organism. For example, a soft robot designed to mimic the movement of an octopus's arm could utilize Nitinol actuators to contract and relax, allowing the robot to navigate through tight spaces or manipulate objects with high precision.
In addition to its bioinspired movements, Nitinol also enhances the compliance and adaptability of soft robots. These systems can adjust their shape in response to changes in the environment, such as when navigating through constrained spaces or handling fragile objects. This flexibility is crucial in applications like search-and-rescue missions, where robots may need to navigate through debris or interact with delicate materials.
Advantages of Nitinol in Soft Robotics
Nitinol's unique properties provide several advantages for soft robotics:
- Shape Memory Effect (SME): The ability to return to a pre-defined shape upon heating makes Nitinol ideal for creating actuators that can mimic natural muscle movements.
- High Power-to-Weight Ratio: Nitinol actuators are lightweight, making them perfect for applications where size and weight are important factors, such as in wearable devices or micro-robotics.
- Flexibility and Softness: Nitinol can bend, stretch, and compress, making it ideal for creating soft, flexible robots that can perform complex motions.
- Energy Efficiency: Nitinol actuators consume relatively low amounts of energy compared to traditional actuators, which is especially important in applications like wearable robotics or medical devices that rely on portability and prolonged use.
- Durability: Nitinol is resistant to wear and fatigue, which makes it suitable for applications that require long-lasting performance.
Challenges and Future Directions
While Nitinol shows great promise in soft robotics, there are still challenges that need to be addressed. For one, Nitinol's response time to thermal or electrical stimulation can sometimes be slow, which can limit its application in fast-moving systems. Additionally, while Nitinol is durable, it can suffer from fatigue after repeated use, which means that engineers must carefully design systems to ensure long-term reliability.
Looking to the future, research is focused on improving the efficiency of Nitinol actuators, including enhancing their response times and increasing their mechanical strength. There is also ongoing work to create hybrid systems that combine Nitinol with other smart materials to create even more advanced actuators for soft robotics.
Conclusion
Nitinol has proven to be a game-changer in the world of soft robotics. From artificial muscles and microscale grippers for surgical tools to wearable robots for rehabilitation and human augmentation, the potential applications of Nitinol are vast and varied. For more shape memory alloys, please check Advanced Refractory Metals(ARM).
Reference:
[1] Caasenbrood, Brandon & Pogromsky, Alexander & Nijmeijer, Henk. (2024). Sorotoki: A Matlab Toolkit for Design, Modeling, and Control of Soft Robots. IEEE Access. PP. 1-1. 10.1109/ACCESS.2024.3357351.
{{item.content}}
LEVE A REPLY
{{item.children[0].content}}
{{item.content}}






