Application of Niobium in the Steel Industry

The application fields of niobium can be divided into the steel industry and the non-steel industry. The former accounts for more than 85% of the world's niobium consumption, while the latter accounts for less than 15%. In this article, let's take a closer look at the application of niobium in the steel industry.

Fig. 1 Application of Niobium in the Steel Industry
The Effect of Niobium Addition in Alloy Steel
Niobium is one of the important alloying elements of steel. Adding a very small amount of niobium to the steel can greatly increase its strength, and improve its mechanical and welding properties, and corrosion resistance. The application of niobium steel is very extensive, covering many sectors such as bridges, construction, heavy machinery, ships, rails, automobiles, tractors, internal combustion engines, steam turbines, drilling equipment, large boilers, tools, and molds.
Further reading: 10 Important Uses of Niobium
Here are the key findings from the experiment on the effects of niobium addition in alloy steel:[1]
- Grain Refinement: Niobium significantly refined the prior austenite grain size. The average grain size decreased from 15.9 μm in the niobium-free sample to 10.1 μm with 0.073 wt% Nb addition, indicating effective grain boundary pinning by Nb(C,N) precipitates.
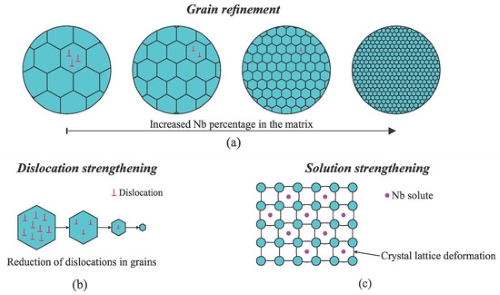
Fig. 2 Strengthening mechanisms due to Nb addition: (a) grain refinement, (b) dislocation strengthening, and (c) solution strengthening.
- Phase Transformation and Microstructure: Niobium delayed phase transformation and promoted the formation of a bainitic microstructure. The Nb-bearing steel contained a higher fraction of bainite and smaller martensite-austenite (M-A) constituents, contributing to better toughness.
- Mechanical Properties:
- Tensile Strength: Increased from 961 MPa to 1026 MPa with Nb addition.
- Yield Strength: Increased from 902 MPa to 992 MPa.
- Elongation: Slightly decreased but remained acceptable (from 15.3% to 14.2%).
- Impact Toughness: Significantly improved, with impact energy increasing from 33 J to 71 J.
- Strengthening Mechanisms: The improvements in strength and toughness were attributed to:
- Grain refinement.
- Enhanced precipitation hardening due to fine Nb(C,N) particles.
- Delayed transformation leading to finer bainite structures.
- Fracture Behavior: The Nb-containing steel exhibited more ductile fracture features (finer and deeper dimples) compared to the Nb-free steel, indicating improved toughness and fracture resistance.
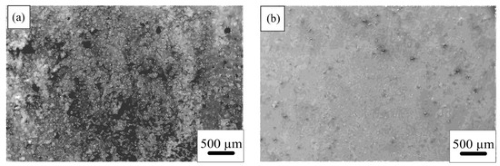
Fig. 3 Corrosion products on the surface of the (a) Nb-free steel and (b) Nb steel samples after 240 h of immersion in H2S. Adapted from Liu et al.; the figure was vectorized using the free software Inkscape.
Niobium in the Steel Industry
--Application of Niobium in Alloy Steel
Low-alloy high-strength steel uses the largest amount of niobium, accounting for more than 80% of the niobium used in the steel industry, and generally contains 0.02-0.05% niobium. Adding a small amount of niobium to form stable carbides and carbonitrides to refine the crystal grains and the precipitation of niobium carbide can improve the strength and creep resistance of the steel.
In addition to niobium-containing low-alloy steels, there are also niobium-containing high-alloy steels. The additives of high alloy steel containing niobium are generally metal niobium bars or ferroniobium with 50-70% niobium. Niobium-containing high-alloy steel includes stainless steel, heat-resistant steel, and corrosion-resistant steel. For example, lCrllCobMnVNbBN steel has been used in the 8-11 stage turbine discs and 9-12 stage blades of aero engines; OCr13si4NbRE steel is resistant to corrosion by oxidizing media and has been used in the valves and pump bodies of concentrated nitric acid production equipment. The use of niobium-containing stainless steel electrodes has been expanding in recent years.
--Application of Niobium in Cast Iron
Adding a small amount of niobium to cast iron can promote graphitization, reduce casting cracks and improve the wear resistance of castings, and significantly improve the toughness and strength of iron. Cylinder liners and piston rings made of niobium-containing cast iron (containing about 0.3% Nb) can improve their wear resistance and service life.
Other Niobium Products
| Niobium Product | Application | Technical Attributes / Benefits |
| HSLA Ferroniobium (~65% Nb) | High-strength low-alloy steel for pipelines, vehicles, buildings, ships, railroads | Doubles strength and toughness via grain refinement; enables weight reduction |
| Niobium Oxide | Lithium niobate filters, camera lenses, display coatings, ceramic capacitors | High refractive index, high dielectric constant, enhances light transmittance |
| Niobium Carbide | Cutting tool compositions | Controls grain growth; high-temperature deformation resistance |
| Niobium Powder | Niobium capacitors in electronic circuits | High dielectric constant; stable oxide dielectric |
| Niobium Metal (plate, wire, etc.) | Sputtering targets, cathodic protection, chemical processing equipment | Excellent corrosion, oxidation, and creep resistance; high-temperature stability |
| Nb-Ti / Nb-Sn Alloys | Superconducting magnets (MRI, maglev trains, physics experiments) | Zero electrical resistance at cryogenic temperatures (below -268.8°C) |
| Nb-1% Zirconium Alloy | Sodium vapor lamps, chemical processing | Corrosion resistance, oxygen fixation, embrittlement resistance |
| Vacuum-Grade Fe-Nb / Ni-Nb | Superalloys in turbine blades (jet engines, land turbines, Inconel alloys) | Increased resistance to high temperatures, corrosion, oxidation, and erosion; improved creep resistance |
Conclusion
Thank you for reading our article and we hope it can help you have a better understanding of the application of niobium in the steel industry. If you want to learn more about niobium and other types of refractory metals, we would like to advise you to visit Advanced Refractory Metals (ARM) for more information.
Reference:
[1] Benedito, A.V.; Benedetty Torres, C.A.; Silva, R.M.d.C.; Krahl, P.A.; Cardoso, D.C.T.; Silva, F.d.A.; Martins, C.H. Effects of Niobium Addition on the Mechanical Properties and Corrosion Resistance of Microalloyed Steels: A Review.
{{item.content}}
LEVE A REPLY
{{item.children[0].content}}
{{item.content}}






