A Detailed Guide to Nickel Alloys

What Are Nickel Alloys?
Nickel alloys are metallic materials primarily composed of nickel, often combined with other elements such as chromium, iron, molybdenum, copper, or cobalt. These combinations are meticulously engineered to amplify properties like strength, corrosion resistance, heat resistance, and mechanical toughness.
Nickel itself is a ductile, corrosion-resistant metal. When alloyed, it transforms into a remarkably versatile material that performs exceptionally in high-stress and high-temperature environments. As a result, nickel alloys are essential across a range of demanding industries including aerospace, marine, chemical processing, electronics, and power generation.

Fig. 1 Nickel Alloy Products
Key Characteristics of Nickel Alloys
Nickel alloys stand out due to a collection of distinctive traits, which make them the materials of choice in extreme operating conditions:
- Exceptional Corrosion Resistance
Monel 400, for instance, exhibits a corrosion rate of less than 1 mm/year in boiling 15% sulfuric acid (ASTM G28 test) and resists seawater corrosion, making it ideal for marine pump shafts and heat exchangers. - High Heat Resistance
Inconel 625 maintains over 90% of its tensile strength even at 980°C (1800°F), making it indispensable in turbines and furnace parts. - Superior Strength and Toughness
Inconel 718 achieves yield strengths around 1034 MPa (150 ksi), with ultimate tensile strength up to 1379 MPa (200 ksi), ideal for jet engine disks and turbine blades. - Oxidation Resistance
Alloy 600 is deployed in nuclear steam generators due to its robustness in high-pressure steam at 600°C. - Excellent Fabricability and Weldability
Hastelloy C-276 can be TIG or MIG welded without cracking, a rare feature for high-strength alloys used in chemical reactors. - Magnetic and Electrical Specialties
Invar 36 has near-zero thermal expansion, making it essential in precision devices, LNG tank walls, and aerospace fixtures. - Creep and Fatigue Resistance
Waspaloy endures over 10,000 hours at 704°C under 690 MPa in creep tests, demonstrating its endurance in high-stress environments. - Controlled Thermal Expansion
Kovar’s expansion characteristics align with borosilicate glass, allowing stress-free sealing in electronics and vacuum tubes.
Further reading: Nickel-Based Alloys: Types and Examples
Common Types of Nickel Alloys
Nickel alloys can be categorized based on their elemental makeup and unique capabilities:
|
Type |
Typical Composition |
Key Characteristics |
Examples |
|
Nickel-Iron Alloys |
~36% Ni, balance Fe |
Low thermal expansion, stable dimensions |
Invar 36, Kovar |
|
Nickel-Copper Alloys |
~63–70% Ni, 20–30% Cu |
Seawater corrosion resistance |
Monel 400, Monel K500 |
|
Nickel-Chromium Alloys |
~60–70% Ni, 15–23% Cr |
Heat resistance and oxidation resistance |
Inconel 600, Inconel 601 |
|
Nickel-Molybdenum Alloys |
~65–70% Ni, 20–30% Mo |
Resistance to reducing acids |
Hastelloy B, Alloy B-2 |
|
Nickel-Chromium-Iron |
~55–75% Ni, 15–21% Cr, 5–10% Fe |
Versatile corrosion and heat resistance |
Inconel 625, Inconel 718 |
|
Nickel-Chromium-Cobalt |
Ni base, 15–25% Cr, 10–20% Co |
Strength and creep resistance at high temperatures |
Waspaloy, Udimet 500 |
|
Nickel-Chromium-Molybdenum |
Ni base, Cr 20–23%, Mo 16–18% |
Dual resistance to oxidizing and reducing environments |
Hastelloy C-276, C-22 |
Overview of Industrial Grades
To meet the diverse demands of industry, nickel alloys are organized into several standardized series, each optimized for specific performance goals:
- Inconel Series
With over 50% nickel content and additions like chromium and molybdenum, Inconel alloys (e.g., Inconel 718) excel in high-temperature and oxidative conditions.
Applications: Jet engines, turbines, nuclear reactors. - Incoloy Series
These contain less nickel and more iron, providing a more economical choice with good corrosion resistance (e.g., Incoloy 800).
Applications: Heat exchangers, power plants, chemical processing. - Monel Series
Comprising mainly nickel and copper, Monel alloys (e.g., Monel K-500) offer outstanding marine corrosion resistance.
Applications: Marine equipment, oil and gas components. - Hastelloy Series
Known for their robust resistance to harsh chemicals and temperature extremes, Hastelloy alloys (e.g., C-276) are widely used in aggressive chemical environments.
Applications: Chemical reactors, pollution control. - Nickel-Titanium Alloys (Nitinol)
Shape-memory alloys like Nitinol can revert to their original shape and are highly corrosion-resistant and flexible.
Applications: Medical devices, actuators, aerospace couplings.
Here is a detailed list of Common Grades of Nickel Alloys:
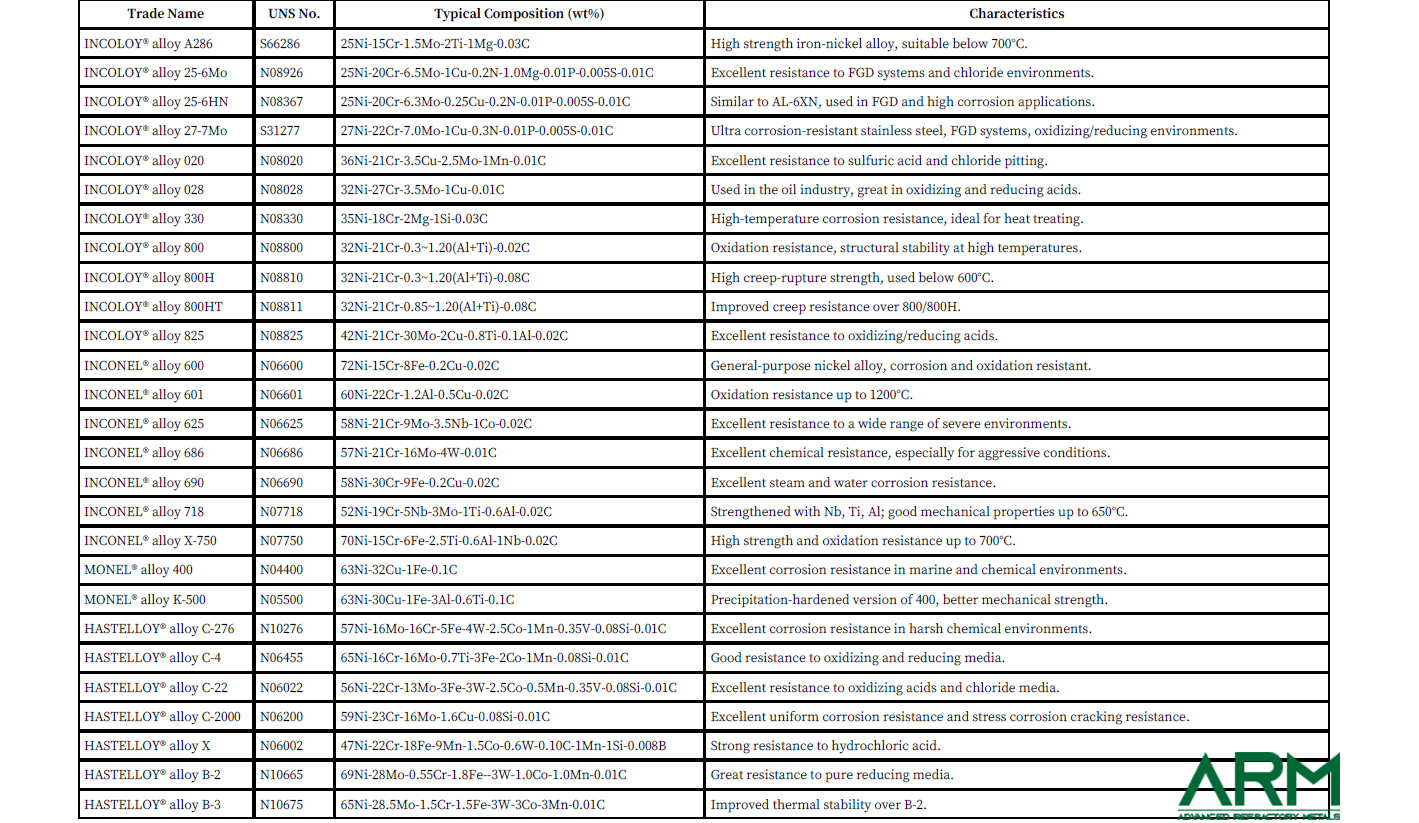
Fig. 2 Common Grades of Nickel Alloys
For pdf version, please click here.
Available Formats of Nickel Alloys
To support these demanding applications, Advanced Refractory Metals (ARM) provides premium-grade nickel alloys in multiple formats:
- Seamless and Welded Pipes & Tubes
- Bars and Wires
- Sheets and Plates
Each format is offered in various grades and dimensions, with custom options available. ARM ensures exceptional quality and tight tolerances, meeting the critical needs of industries ranging from aerospace to chemical processing.
Conclusion
Nickel alloys are indispensable to modern engineering, offering a combination of strength, resistance, and reliability unmatched by many other materials. From the deep sea to outer space, they enable technologies to operate safely under the most extreme conditions. By understanding their composition, characteristics, and applications, engineers and manufacturers can select the ideal alloy to meet their specific challenges—and with trusted suppliers like ARM, they can do so with confidence and precision.
{{item.content}}
LEVE A REPLY
{{item.children[0].content}}
{{item.content}}






