The Effects of Rhenium Addition on Various Alloys
Rhenium (Re), a scarce and high-melting-point metal, has been a subject of intense interest in materials science for its property-strengthening effect on a broad spectrum of alloys. Addition of rhenium to numerous alloy systems has brought about dramatic improvement in mechanical strength, microstructural stability, and corrosion resistance. The multifaceted impacts of rhenium additions to a variety of alloys are discussed here.
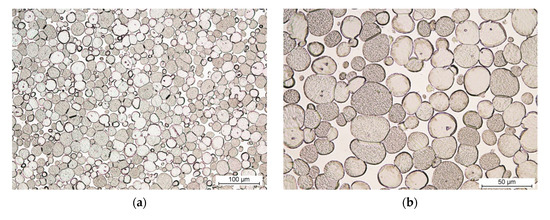
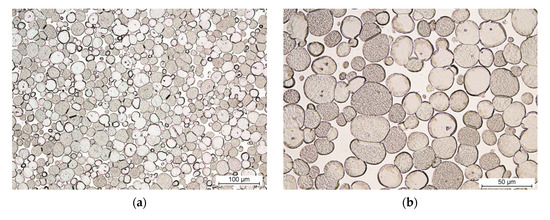
Fig. 1 The microstructure of THA: (a,b) without addition of Re (PR-100)
Credit: Preliminary Study of the Rhenium Addition on the Structure and Mechanical Properties of Tungsten Heavy Alloy
1. Nickel-Based Superalloys
Superalloys based on nickel have been marketed for their strength at elevated temperatures and corrosion resistance, and they have found great suitability in power generation and aerospace applications. It has been established that rhenium addition to these alloys greatly improves their performance.
For example, the addition of 3 wt% Re to nickel-based single-crystal superalloys improves the alloy's life by a factor of ten. This occurs as a result of the decrease in the minimum creep rate and the enhancement in the creep-to-rupture ratio over a range of temperatures (Zhang et al., 2018).
Besides, rhenium additions stabilize the γ′ precipitates in the alloy, resulting in a larger volume fraction and slower coarsening rate. The stabilization is important for the retention of the alloy's strength after long-term exposure at high temperature (Zhang et al., 2018; Mohamed et al., 2021).
But it should be noted that much as rhenium enhances some properties, it could influence others as well. For example, atomistic simulations have shown that rhenium dopants on {100} phase interfaces can activate mobile partial dislocations, which increase creep and lead to larger creep strains (Ma et al., 2021).
Further reading: 6 Interesting Facts about Rhenium
2. Tungsten Heavy Alloys (WHAs)
Tungsten heavy alloys, normally tungsten alloyed with nickel and iron, find application in those areas where both high density and strength are required. Rhenium addition in WHAs has been investigated in order to improve their mechanical properties.
Research has found that additions of rhenium cause grain refinement, increased hardness, and improved strength in tungsten heavy alloys—although these properties are achieved at the expense of ductility (Wang et al., 2021).
In addition, when they are processed through spark plasma sintering, rhenium-alloyed WHAs exhibit better microstructures and mechanical properties compared to unalloyed ones (Wang et al., 2021).
3. Titanium Aluminide Alloys
Titanium aluminide alloys are lightweight alloys with high high-temperature strength and are commonly used in aerospace. TiAl alloys with rhenium addition have also been found to be promising.
For instance, rhenium addition to Ti-48Al-2Cr-2Nb alloys improves their compressive strength to as much as 2282 MPa for γ-TiAl−2Re alloy (Kowalski et al., 2021).
Additionally, the introduction of rhenium affects the microstructure by refining it in the lamellar colonies and encouraging even distribution, which is responsible for the high mechanical properties (Kowalski et al., 2021).
4. Oxide Dispersion Strengthened (ODS) Ferritic Steels
ODS ferritic steels have higher high-temperature strength and radiation resistance and are being considered for nuclear applications. The influence of rhenium additions on these steels has been examined to improve their performance further.
Addition of rhenium to 15Cr-1Mo ODS ferritic steels has been found to enhance their tensile strength and high-temperature creep rupture performance. This is due to the solid-solution strengthening effect of rhenium and its role in oxide particle dispersion in the steel matrix (Kim et al., 2021).
5. Cobalt-Based Alloys
Cobalt alloys find application where wear resistance and high temperature strength are needed. The effect of rhenium addition to these alloys has been investigated in the context of its effect on oxidation resistance and microstructure.
It has been shown that rhenium addition in Co-Cr-Ta-Ti-C alloys causes precipitation and growth of a CoCr-rich σ-phase. Although this may be useful for certain mechanical properties, it may influence the oxidation behavior of the alloy. In particular, the generation of volatile ReO₃ can result in catastrophic rhenium depletion during oxidation. To counteract this, the addition of more than 25 at% chromium to the alloy will create a protective Cr₂O₃ scale that prevents Re oxide evaporation and promotes oxidation resistance (Wang et al., 2021).
Conclusion
The incorporation of rhenium into various alloy systems has demonstrated considerable potential for enhancing mechanical strength, microstructural stability, and corrosion resistance.
In nickel-based superalloys, rhenium improves creep resistance and stabilizes precipitates. In tungsten heavy alloys, it refines grain structures and strengthens, albeit with reduced ductility. Titanium aluminide alloys are enhanced by improved compressive strength and refined microstructures. ODS ferritic steels enjoy improved high-temperature properties, and cobalt-based alloys undergo tailored modification of oxidation behavior that can be managed by composition control.
While the benefits of rhenium are obvious, its effects must be considered holistically because gains in one area often come with trade-offs in another. Therefore, careful alloy design and processing are essential to fully leverage the advantages that rhenium offers.
References
- Kim, J. H., et al. (2021). Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of ODS Ferritic Steels with Rhenium Addition. PubMed. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34885520/
- Kowalski, M. J., et al. (2021). The Impact of Rhenium Addition on the Microstructure and Properties of TiAl Alloys. Materials, 14(23), 7365. https://www.mdpi.com/1996-1944/14/23/7365
- Ma, Z., et al. (2021). Atomistic study of rhenium segregation at γ/γ′ interface in Ni-based superalloys. PMC. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC10779487/
- Mohamed, H. M., et al. (2007). Creep deformation and microstructure of rhenium-containing single crystal superalloys. NASA Technical Reports. https://ntrs.nasa.gov/citations/20070006530
- Wang, C., Zhang, X., Liu, Z., Fang, Y., & Ren, X. (2021). Effect of Rhenium addition on tungsten heavy alloys processed through spark plasma sintering. Journal of Advanced Ceramics, 10(4), 778–789. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40145-021-0453-4
- Zhang, J., Yuan, Y., Zou, Y., & Wang, H. (2018). Effect of Rhenium Addition on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of a Ni-Based Superalloy Fabricated by Selective Laser Melting. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 49(11), 5194–5207. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-018-4926-3
{{item.content}}
LEVE A REPLY
{{item.children[0].content}}
{{item.content}}






