Tantalum Powders: Spherical, Capacitor, and More
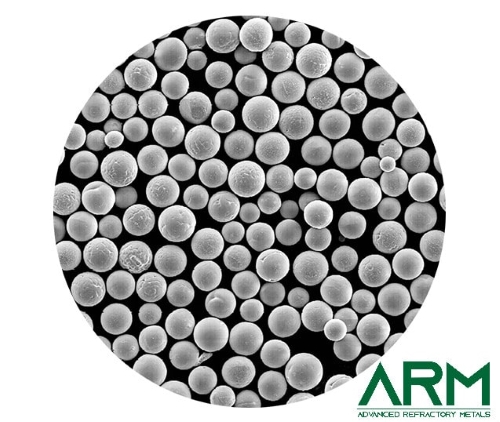
Tantalum powder is known for its excellent corrosion resistance, high melting point, and biocompatibility. The classification of Ta powders is based on several factors, including purity, particle morphology, size distribution, and intended applications. Understanding these classifications is essential for selecting the right type of Ta powder for a specific use.
Classification by Purity
Purity is one of the most critical factors in determining the performance of tantalum powders, particularly in high-tech applications such as electronics and medical devices.
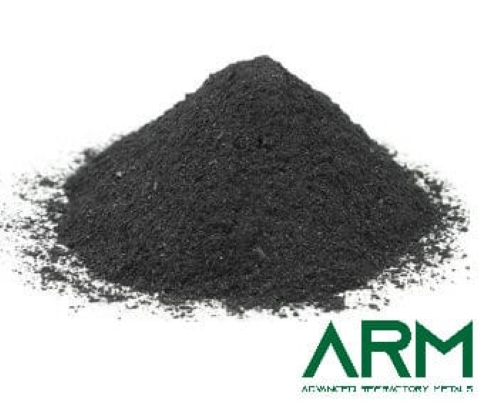

Ta powders are generally classified into two main purity levels.
- High-purity tantalum powders, which contain at least 99.9% tantalum, are commonly used in electronic components, particularly capacitors.
- Ultra-high-purity tantalum powders, with a purity exceeding 99.99%, are essential for semiconductor applications, medical implants, and aerospace components where even trace impurities can significantly impact performance.
Impurities such as oxygen, nitrogen, carbon, and metallic contaminants must be carefully controlled, as they can alter the mechanical, electrical, and corrosion-resistant properties of the final product.
Classification by Particle Morphology
The morphology of tantalum powders is determined by the production method used and influences their packing density, flowability, and sintering behavior.
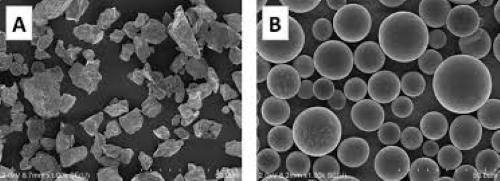
The three most common forms of Ta powder are spherical, angular or irregular, and flake.
- Spherical tantalum powders are produced through gas atomization or plasma spheroidization, resulting in uniform, round particles with excellent flowability. This makes them ideal for additive manufacturing, biomedical implants, and aerospace coatings.
- In contrast, angular or irregular tantalum powders, typically produced via mechanical milling or chemical reduction, have lower flowability but offer superior compaction properties.
These powders are widely used in the production of tantalum capacitors and sintered structural components. Flake Ta powders, characterized by their large surface area, are optimized for high-capacitance electronic applications.
Classification by Particle Size Distribution
Particle size distribution plays a crucial role in determining the usability of Ta powders in different applications.
- Nano and submicron tantalum powders, typically smaller than 1 micrometer, are used in advanced electronics, catalysts, and specialized coatings.
- Fine tantalum powders, ranging from 1 to 10 micrometers, are preferred for capacitor applications due to their high surface area.
- Medium-sized powders, with particle sizes between 10 and 100 micrometers, are commonly used in metallurgical applications and protective coatings.
- Coarse tantalum powders, larger than 100 micrometers, are suitable for thermal spray coatings, 3D printing, and sintered components in aerospace and industrial applications.
Classification by Application
Ta powders are classified based on their intended applications, each requiring specific characteristics in terms of purity, particle size, and morphology.
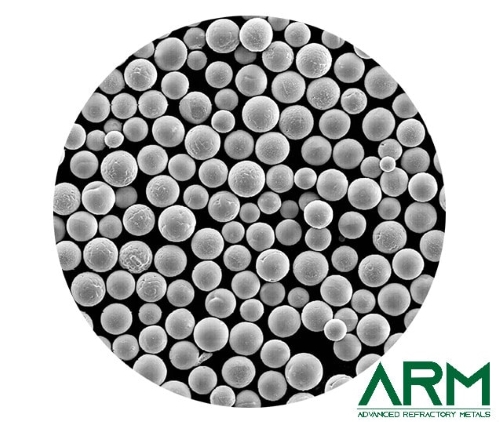
- Capacitor-grade tantalum powders are specifically engineered for electronic components, where their high surface area allows for efficient charge storage. These powders require exceptionally low levels of impurities to ensure optimal electrical performance.
- Metallurgical-grade tantalum powders, on the other hand, are used in superalloys and corrosion-resistant coatings. These powders provide high mechanical strength and oxidation resistance, making them suitable for high-temperature environments such as jet engines and chemical processing equipment.
- Medical-grade tantalum powders must meet stringent purity requirements to ensure biocompatibility. They are used in bone implants, dental applications, and orthopedic prosthetics. Tantalum’s excellent osseointegration properties make it a preferred material for medical implants, as it promotes bone growth around the implanted structure.
- Another important classification is additive manufacturing (AM) grade tantalum powder, which is primarily spherical in shape to ensure high flowability and uniform layer deposition in 3D printing processes. These powders are widely used in the production of custom medical implants, aerospace parts, and industrial components.
- Thermal spray and coating-grade tantalum powders are designed for use in protective coatings that enhance the durability of surfaces exposed to extreme conditions. These powders are applied in chemical reactors, semiconductor manufacturing equipment, and high-temperature tools to provide corrosion and wear resistance.
Conclusion
Tantalum powders are classified based on their purity, morphology, particle size distribution, and intended applications. High-purity and ultra-high-purity Ta powders are required for electronics and medical devices, while metallurgical-grade powders provide strength and corrosion resistance for aerospace and industrial uses. Understanding these classifications ensures that Ta powders are used effectively in industries that demand high-performance materials. For more tantalum products, please check Advanced Refractory Metals (ARM).
{{item.content}}
LEVE A REPLY
{{item.children[0].content}}
{{item.content}}






