The Versatility of Tantalum Marker Bands: Applications and Benefits

Introduction
When it comes to medical procedures, accuracy, and precision are of utmost importance. Whether in radiology, cardiology, or other fields, healthcare professionals rely on markers to enhance visibility and provide crucial reference points. Tantalum marker bands have emerged as a valuable tool in various medical applications, thanks to their unique properties and versatility. In this article, we will explore the applications and benefits of tantalum marker bands and their role in improving medical procedures.

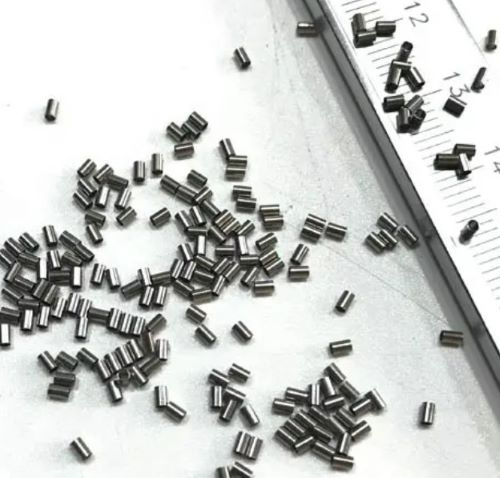
Tantalum Marker Bands
Understanding Tantalum Marker Bands
Tantalum marker bands are small, cylindrical devices made from tantalum, a rare and lustrous metal known for its exceptional biocompatibility and radiopacity. Tantalum is a corrosion-resistant metal with a high melting point. It is biocompatible as well, meaning it does not cause adverse reactions or toxicity in the human body. These characteristics make tantalum an excellent choice for marker bands used in medical procedures to mark specific anatomical locations, guide surgical instruments, and aid in the precise localization of tumors, lesions, or other targeted areas within the body.
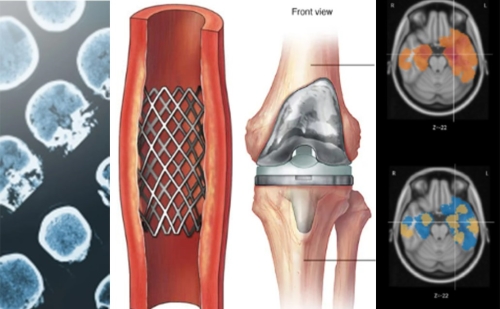
Applications of Tantalum Marker Bands
--Radiology Applications
Tantalum marker bands play a crucial role in radiology, particularly in the field of interventional radiology. When placed strategically within the body, these marker bands can be easily detected by X-rays, CT scans, or fluoroscopy. They are often placed on catheters, guidewires, or other medical devices to enhance visibility and provide clear reference points during imaging procedures.
One common application of tantalum marker bands is in interventional cardiology. These bands are used in stents to ensure accurate placement within the blood vessels, allowing physicians to precisely navigate and treat blockages or other cardiac conditions.
Additionally, these marker bands are used in endovascular procedures, such as embolization or coil placement. By strategically positioning the marker bands, physicians can precisely track the placement of devices, ensuring optimal outcomes for patients.
Related reading: Application of Tantalum Marker Band in Medical Devices
--Orthopedic Applications
Tantalum marker bands are also utilized in orthopedic procedures, particularly in joint replacement surgeries. These marker bands are placed on implants, such as artificial hips or knees, to aid in accurate positioning during surgery and postoperative imaging. By using tantalum marker bands, surgeons can ensure proper alignment and joint function, leading to better patient outcomes.
--Diagnostic Procedures
Tantalum marker bands play a crucial role in diagnostic procedures where precise tracking and visualization are essential. Here are a few examples:
- Localization of Tumors: In procedures such as preoperative tumor localization or biopsy, tantalum marker bands are used to mark the precise location of tumors. By placing a marker band near the tumor site, radiologists can accurately identify and guide the biopsy needle or surgical instruments to the target area, ensuring the procedure is performed with precision.
- Endoscopy and Gastrointestinal Procedures: Tantalum marker bands are employed in gastrointestinal procedures to help locate lesions, strictures, or abnormal areas. For instance, in capsule endoscopy, marker bands may be placed near areas of interest to assist in subsequent analysis and interpretation of the captured images.
--Surgical Procedures
In surgical procedures, tantalum marker bands serve as invaluable tools. They are placed near critical structures, such as blood vessels or nerves, so surgeons can minimize the risk of inadvertent injury during complex operations. This not only improves patient safety but also helps achieve optimal surgical outcomes.
Benefits of Tantalum Marker Bands
The use of tantalum marker bands offers several benefits in medical procedures:
- Enhanced Visibility: Tantalum is highly radiopaque. That is to say, it appears very bright and clear in imaging studies. This property improves visibility and enables healthcare professionals to precisely locate and track the position of medical devices or implants during procedures.
- Biocompatibility: Tantalum is well-tolerated by the human body, making it an ideal material for marker bands. It does not cause adverse reactions, inflammation, or toxicity, ensuring patient safety and compatibility.
- Time and Cost Efficiency: The enhanced visualization provided by tantalum marker bands allows medical professionals to work efficiently, minimizing the overall time required for interventions. Besides, tantalum marker bands are cost-effective alternatives to traditional medical marker bands made from gold, platinum, tantalum, iridium, or tungsten.
- Long-term Stability: Tantalum marker bands are durable and provide long-term stability. They are resistant to corrosion and degradation, ensuring their visibility and integrity over time. This longevity is particularly important in cases where long-term follow-up or monitoring is required.
- Versatility: These bands come in various sizes and configurations to suit different medical devices and procedures. This versatility allows healthcare professionals to customize their use according to specific patient needs and procedural requirements.
Conclusion
Tantalum marker bands have proven to be a valuable asset in radiology, orthopedics, and other medical procedures, offering enhanced visibility, biocompatibility, and lower cost. Their applications contribute to accurate positioning, improved outcomes, and better patient care. As technology continues to advance, tantalum marker bands will continue to play a vital role in ensuring accuracy and enhancing medical procedures across various specialties.
Advanced Refractory Materials (ARM) is a worldwide supplier of tantalum products. Hope that you can find the perfect tantalum marker bands on the website.
{{item.content}}
LEVE A REPLY
{{item.children[0].content}}
{{item.content}}






